Machine Studying (ML) is a subset of synthetic intelligence (AI) that facilities on creating algorithms to study from knowledge and make predictions or selections without having detailed programming for every process. Quite than adhering to strict tips, ML fashions acknowledge patterns and improve their effectiveness as time progresses.
Greedy these phrases and their associated algorithms is essential for using machine studying successfully in numerous fields, spanning healthcare and finance to automation and synthetic intelligence functions.
On this article, we are going to discover totally different varieties of Machine Studying algorithms, how they perform, and their functions in the true world to deepen your comprehension of their significance and sensible implementation.
What’s a Machine Studying Algorithm?
A machine studying algorithm consists of guidelines or mathematical fashions that permit computer systems to acknowledge patterns in knowledge and generate predictions or selections with out direct programming. These algorithms analyze enter knowledge, acknowledge connections, and improve effectivity as time progresses.
How They Work:
- Practice on a dataset to acknowledge patterns.
- Take a look at on new knowledge to guage efficiency.
- Optimize by adjusting parameters to enhance accuracy.
Machine studying algorithms drive functions corresponding to suggestion programs, fraud detection, and autonomous autos.
Kinds of Machine Studying Algorithms
Machine Studying algorithms may be categorized into 5 varieties:
- Supervised Studying
- Unsupervised Studying
- Reinforcement Studying
- Semi-Supervised Studying
- Deep Studying Algorithms
1. Supervised Studying
In supervised studying, the mannequin is skilled utilizing a labeled dataset, indicating that each coaching instance comprises an input-output pair. This algorithm learns to affiliate inputs with the suitable outputs primarily based on historic knowledge.
Frequent Supervised Studying Algorithms:
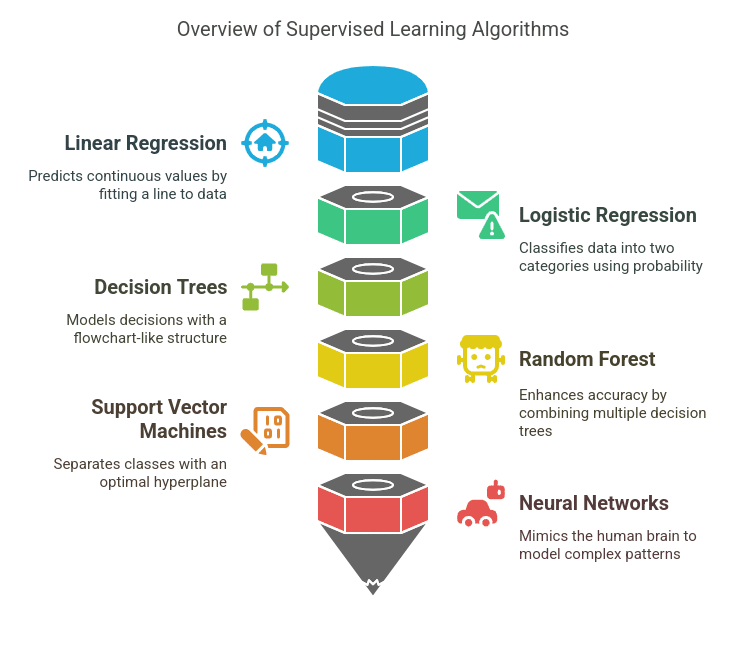

A. Linear Regression
Linear Regression is a basic algorithm used to foretell steady numerical values primarily based on enter options. It really works by becoming a straight line (y=mx+b) to the info that greatest represents the connection between the impartial and dependent variables.
- Instance: Estimating residence values contemplating parts corresponding to space, bed room rely, and geographic place.
- Key Idea: It reduces the discrepancy between noticed and estimated values by using the least squares approach
B. Logistic Regression
Although its title suggests in any other case, Logistic Regression is employed for classification as a substitute of regression. It makes use of the sigmoid perform to remodel predicted values into a variety of 0 to 1, which makes it appropriate for binary classification points.
- Instance: Figuring out whether or not an electronic mail is spam or not primarily based on the presence of particular key phrases.
- Key Idea: Makes use of chance to categorise knowledge factors into two classes and applies a threshold (e.g., 0.5) to make selections.
C. Determination Bushes
A Determination Tree is a mannequin resembling a flowchart, with every node symbolizing a function, each department indicating a call, and every leaf denoting an final result. It’s able to managing each classification and regression duties.
- Instance: A financial institution decides whether or not to approve a mortgage primarily based on earnings, credit score rating, and employment historical past.
- Key Idea: Splits knowledge primarily based on function situations to maximise data acquire utilizing metrics like Gini Impurity or Entropy.
D. Random Forest
Random Forest is an ensemble studying approach that creates a number of determination timber and merges their outcomes to reinforce accuracy and reduce overfitting.
- Instance: Predicting whether or not a buyer will churn primarily based on transaction historical past, demographics, and interactions with customer support.
- Key Idea: Makes use of bootstrap aggregating (bagging) to generate numerous timber and averages their predictions for stability.
E. Help Vector Machines (SVM)
SVM is a strong classification algorithm that finds the optimum hyperplane to separate totally different lessons. It’s notably helpful for datasets with clear margins between classes.
- Instance: Classifying handwritten digits within the MNIST dataset.
- Key Idea: Makes use of kernel features (linear, polynomial, RBF) to map knowledge into larger dimensions for higher separation.
F. Neural Networks
Neural Networks mimic the human mind, consisting of a number of layers of interconnected neurons that study from knowledge. They’re extensively used for deep studying functions.
- Instance: Picture recognition in self-driving vehicles to detect pedestrians, visitors indicators, and different autos.
Functions of Supervised Studying:
- E-mail Spam Filtering
- Medical Analysis
- Buyer Churn Prediction
2. Unsupervised Studying
Unsupervised studying offers with knowledge that doesn’t have labeled responses. The algorithm finds hidden patterns and constructions within the dataset.
Frequent Unsupervised Studying Algorithms:
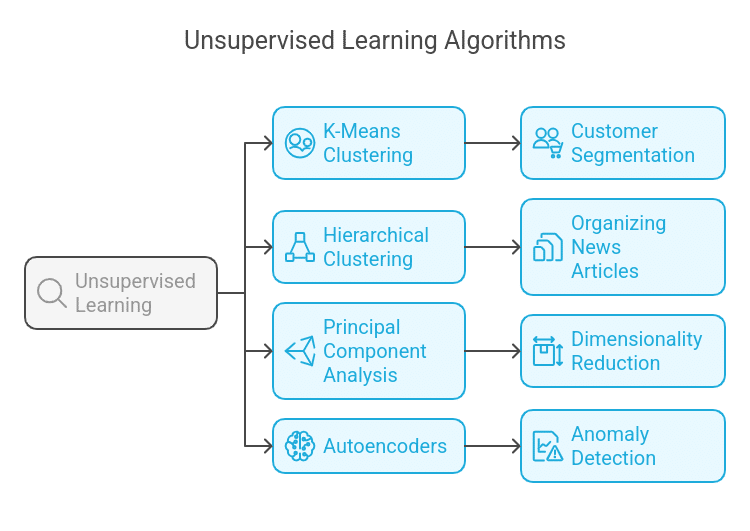

A. Ok-Means Clustering
Ok-Means is a well-liked clustering algorithm that teams related knowledge factors into Ok clusters. It assigns every level to the closest cluster centroid and updates centroids iteratively to attenuate variance inside clusters.
- Instance: Buyer segmentation in e-commerce, the place customers are grouped primarily based on their buying habits.
- Key Idea: Makes use of the Euclidean distance to assign knowledge factors to clusters and updates centroids till convergence.
B. Hierarchical Clustering
Hierarchical Clustering builds a hierarchy of clusters utilizing both Agglomerative (bottom-up) or Divisive (top-down) approaches. It creates a dendrogram to visualise relationships between clusters.
- Instance: Organizing information articles into topic-based teams with out predefined classes.
- Key Idea: Makes use of distance metrics (e.g., single-linkage, complete-linkage) to merge or break up clusters.
C. Principal Part Evaluation (PCA)
PCA is a technique for decreasing dimensionality that converts high-dimensional knowledge right into a lower-dimensional house whereas sustaining key data. It finds the principal parts, that are the instructions of most variance.
- Instance: Decreasing the variety of options in a picture dataset whereas retaining essential patterns for machine studying fashions.
- Key Idea: Makes use of eigenvectors and eigenvalues to undertaking knowledge onto fewer dimensions whereas minimizing data loss.
D. Autoencoders
Autoencoders are a kind of neural community used for function studying, compression, and anomaly detection. They encompass an encoder (compressing enter knowledge) and a decoder (reconstructing the unique knowledge).
- Instance: Detecting fraudulent transactions by figuring out uncommon patterns in monetary knowledge.
- Key Idea: Makes use of a bottleneck layer to seize necessary options and reconstructs knowledge utilizing imply squared error (MSE) loss.
Functions of Unsupervised Studying:
- Buyer Segmentation
- Anomaly Detection in Fraud Detection
- Recommender Programs (e.g., Netflix, Amazon)
Perceive the important thing variations between Supervised and Unsupervised Studying and the way they impression machine studying fashions.
3. Reinforcement Studying
Reinforcement studying (RL) includes an agent studying to work together with an atmosphere to maximise the overall sum of rewards over time.
Key Ideas in Reinforcement Studying:
- Agent – The entity that takes actions.
- Atmosphere – The world through which the agent operates.
- Actions – Selections the agent could make.
- Rewards – Suggestions alerts guiding the agent.
Frequent Reinforcement Studying Algorithms:
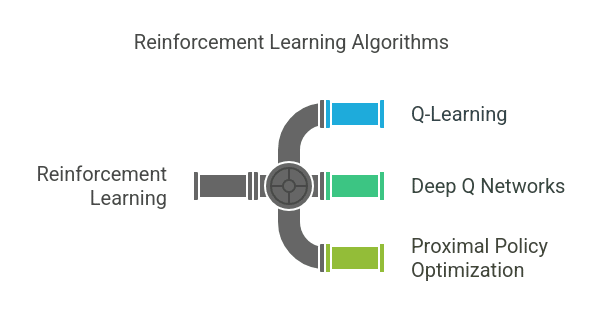

A. Q-Studying
Q-learning is a reinforcement studying algorithm and not using a mannequin that develops an excellent action-selection coverage by a Q-table. It follows the Bellman equation to replace the Q-values primarily based on rewards obtained from the atmosphere.
- Instance: Coaching an AI agent to play a easy recreation like Tic-Tac-Toe by studying which strikes result in victory over time.
- Key Idea: Makes use of the ε-greedy coverage to steadiness exploration (making an attempt new actions) and exploitation (selecting the best-known motion).
B. Deep Q Networks (DQN)
DQN is an extension of Q-Studying that leverages deep neural networks to approximate the Q-values, making it appropriate for high-dimensional environments the place sustaining a Q-table is impractical.
- Instance: Educating an AI to play Atari video games, like Breakout, the place uncooked pixel knowledge is used as enter.
- Key Idea: Makes use of expertise replay (storing previous experiences) and a goal community (stabilizing coaching) to enhance studying.
C. Proximal Coverage Optimization (PPO)
PPO is a policy-based reinforcement studying algorithm that optimizes actions utilizing a belief area method, guaranteeing secure updates and stopping massive, destabilizing coverage modifications.
- Instance: Coaching robotic arms to know objects effectively or enabling recreation AI to strategize in complicated environments.
- Key Idea: Makes use of clipped goal features to stop overly aggressive updates and enhance coaching stability.
Functions of Reinforcement Studying:
- Sport Taking part in (e.g., AlphaGo, OpenAI Fitness center)
- Robotics Automation
- Autonomous Automobiles
Perceive the basics of Reinforcement Studying and get it to make selections in AI and robotics.
4. Semi-Supervised Studying
Semi-supervised studying falls between supervised and unsupervised studying, the place solely a small portion of the dataset is labeled, and the remainder is unlabeled.
Functions:
- Speech Recognition
- Textual content Classification
- Medical Picture Evaluation
5. Deep Studying Algorithms
Deep Studying is a site of Machine Studying that includes neural networks with a number of layers (i.e., deep networks) to find subtle attributes of uncooked knowledge.

Fashionable Deep Studying Architectures:
Functions:
Grasp Machine Studying with Python on this free course. Study key ML ideas, algorithms, and hands-on implementation from trade specialists.
Selecting the Proper Machine Studying Algorithm
Choosing the suitable machine studying algorithm depends upon numerous components, together with the character of the info, the issue kind, and computational effectivity.
Listed here are key concerns for selecting the right algorithm:
- Kind of Information: Structured and Unstructured
- Drawback Kind: Classification, Regression, Clustering, or Anomaly Detection
- Accuracy vs. Interpretability: Determination timber are simple to interpret, whereas deep studying fashions are extra correct however extra complicated to know.
- Computational Energy: Some fashions require excessive computational assets (e.g., deep studying).
Experimentation and mannequin analysis utilizing strategies like cross-validation and hyperparameter tuning are essential in choosing the best-performing algorithm.
Uncover the most recent Synthetic Intelligence and Machine Studying Traits shaping the way forward for AI.
Pattern Codes of ML Algorithms in Python
Linear Regression in Python
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import numpy as np
# Pattern Information
X = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).reshape(-1, 1)
y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
# Mannequin Coaching
mannequin = LinearRegression()
mannequin.match(X, y)
# Prediction
print(mannequin.predict([[6]])) # Output: Approx 12
Logistic Regression in Python
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import numpy as np
# Pattern Information
X = np.array([[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]])
y = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1]) # Binary classification
# Mannequin Coaching
mannequin = LogisticRegression()
mannequin.match(X, y)
# Prediction
print(mannequin.predict([[2.5]])) # Output: 0 or 1 primarily based on realized sample
Ok-Means Clustering in Python
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import numpy as np
# Pattern Information
X = np.array([[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4], [8, 9], [9, 10]])
# Ok-Means Mannequin
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2, random_state=0)
kmeans.match(X)
# Output cluster labels
print(kmeans.labels_) # Labels assigned to every knowledge level
Determination Tree Classifier in Python
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
import numpy as np
# Pattern Information
X = np.array([[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]])
y = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1]) # Binary classification
# Mannequin Coaching
mannequin = DecisionTreeClassifier()
mannequin.match(X, y)
# Prediction
print(mannequin.predict([[3.5]])) # Anticipated Output: 1
Help Vector Machine (SVM) in Python
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import numpy as np
# Pattern Information
X = np.array([[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]])
y = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1]) # Binary classification
# Mannequin Coaching
mannequin = SVC(kernel="linear")
mannequin.match(X, y)
# Prediction
print(mannequin.predict([[2.5]])) # Output: 0 or 1
Conclusion
Machine studying algorithms are a algorithm that assist AI programs study and carry out duties. They’re used to find patterns in knowledge or to foretell outcomes from enter knowledge.
These algorithms are the spine of AI-driven options. Realizing these algorithms empowers you to leverage them extra successfully.
Desire a profession in AI & ML?
Our PG Program in AI & Machine Studying builds experience in NLP, GenAI, neural networks, and deep studying. Earn certificates and begin your AI journey immediately!
Steadily Requested Questions
1. What’s the bias-variance tradeoff in machine studying?
The bias-variance tradeoff is a basic idea in ML that balances two sources of error:
- Excessive Bias (Underfitting): The mannequin is just too easy and fails to seize knowledge patterns.
- Excessive Variance (Overfitting): The mannequin is just too complicated and suits noise within the coaching knowledge.
- An optimum mannequin finds a steadiness between bias and variance to generalize properly to new knowledge.
2. What’s the distinction between parametric and non-parametric algorithms?
- Parametric algorithms assume fastened parameters (e.g., Linear Regression, Logistic Regression). They’re sooner however might not seize complicated relationships.
- Non-parametric algorithms don’t assume a hard and fast construction and adapt primarily based on knowledge (e.g., Determination Bushes, Ok-nearest neighbors). They’re extra versatile however require extra knowledge to carry out properly.
3. What are ensemble studying strategies?
Ensemble studying combines a number of fashions to enhance accuracy and cut back errors. Frequent strategies embrace:
- Bagging (e.g., Random Forest) – Combines a number of determination timber for higher stability.
- Boosting (e.g., XGBoost, AdaBoost) – Sequentially improves weak fashions by specializing in complicated circumstances.
- Stacking – Combines totally different fashions and makes use of one other mannequin to mixture outcomes.
Understanding the Ensemble Methodology Bagging and Boosting
4. What’s function choice, and why is it necessary?
Characteristic choice is the method of selecting essentially the most related enter variables for a machine studying mannequin to enhance accuracy and cut back complexity. Methods embrace:
- Filter Strategies (e.g., correlation, mutual data)
- Wrapper Strategies (e.g., Recursive Characteristic Elimination)
- Embedded Strategies (e.g., Lasso Regression)
5. What’s switch studying in machine studying?
Switch studying includes utilizing a pre-trained mannequin on a brand new process with minimal retraining. It’s generally utilized in deep studying for NLP (e.g., BERT, GPT) and laptop imaginative and prescient (e.g., ResNet, VGG). It permits leveraging information from massive datasets with out coaching from scratch.



