On this blogpost, we offer a technical evaluation of CloudScout, a post-compromise toolset utilized by Evasive Panda to focus on a authorities entity and a non secular group in Taiwan from 2022 to 2023. The CloudScout toolset is able to retrieving information from numerous cloud companies by leveraging stolen internet session cookies. Via a plugin, CloudScout works seamlessly with MgBot, Evasive Panda’s signature malware framework.
Key factors of this blogpost:
- The CloudScout toolset was detected in Taiwan, between 2022 and 2023, within the community of a non secular establishment and at a authorities entity.
- CloudScout makes use of stolen cookies, supplied by MgBot plugins, to entry and exfiltrate information saved at numerous cloud companies.
- We analyzed three CloudScout modules, which goal to steal information from Google Drive, Gmail, and Outlook. We consider that at the very least seven further modules exist.
- Hardcoded fields in CloudScout’s internet requests for stealing Outlook e mail messages counsel that the samples concerned had been crafted to focus on Taiwanese customers.
- Every CloudScout module, programmed in C#, is deployed by an MgBot plugin, programmed in C++.
Evasive Panda profile
Evasive Panda (also called BRONZE HIGHLAND, Daggerfly, or StormBamboo) is a China-aligned APT group, working since at least 2012. Evasive Panda’s goal is cyberespionage towards nations and organizations opposing China’s pursuits via independence actions akin to these within the Tibetan diaspora, non secular and educational establishments in Taiwan and in Hong Kong, and supporters of democracy in China. At instances we now have additionally noticed its cyberespionage operations lengthen to nations akin to Vietnam, Myanmar, and South Korea.
Evasive Panda has amassed a powerful listing of assault vectors. We now have seen its operators conduct subtle TTPs akin to supply-chain and watering-hole assaults, and DNS hijacking; as well as, they’ve abused the newest CVEs affecting Microsoft Workplace, Confluence, and internet server functions. The group additionally demonstrates a powerful functionality for malware improvement, which is showcased in its deep assortment of multiplatform backdoors for Home windows, macOS, and Android. For Home windows, its most-used instruments are MgBot (since 2012; a {custom} malware framework consisting of a major implant and eight at the moment identified plugins as detailed in our WLS blogpost) and the extra lately developed Nightdoor (described in one other WLS blogpost; a feature-rich backdoor that makes use of public cloud companies for C&C communications).
Overview
In early 2023, we detected Evasive Panda deploy three beforehand unknown .NET modules (internally named CGD, CGM, and COL) at a authorities entity in Taiwan. These modules are designed to entry public cloud companies akin to Google Drive, Gmail, and Outlook by hijacking authenticated internet classes. This system depends on stealing cookies from an internet browser database, then utilizing them in a selected set of internet requests to achieve entry to cloud companies. In contrast to stolen credentials, which can be blocked by safety features akin to two-factor authentication (2FA) and IP monitoring, stolen internet session cookies permit the attacker to retrieve information saved within the cloud, proper from the sufferer’s machine. In 2023, Google launched the Device Bound Session Credentials (DBSC) challenge on GitHub and, in 2024, the App-Bound Encryption function within the Chrome 127 replace. These are protecting measures towards cookie-theft malware, akin to CloudScout, and will doubtlessly render this toolset out of date.
Additional code evaluation of the three modules reveals an underlying improvement framework, codenamed CloudScout by its builders. On this blogpost, we offer an in depth evaluation of this modular framework programmed in C#. To the very best of our data, the CloudScout toolset has not beforehand been documented publicly.
Victimology
In response to ESET telemetry, CloudScout was noticed in two incidents concentrating on Taiwan:
- In Might 2022, the community of a Taiwanese non secular establishment was compromised with MgBot and Nightdoor. On this incident, MgBot was used to put in a plugin that deploys a CloudScout module.
- In February 2023, CloudScout modules and the Nightdoor implant had been detected at what we suspect is a Taiwanese authorities entity.
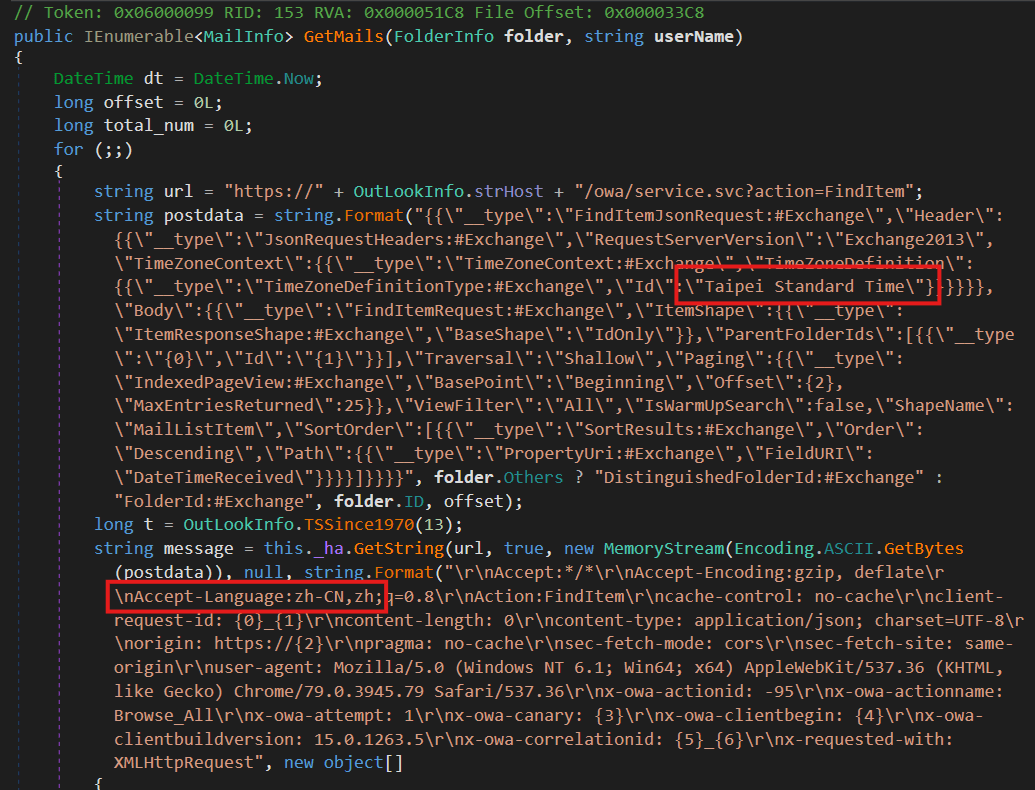
Moreover, we present in some hardcoded HTTP requests the inclusion of Taipei Normal Time because the time zone and zh-CN because the language pack (as proven in Determine 1). Each counsel that these samples had been crafted to focus on Taiwanese customers.
Technical evaluation
CloudScout is a .NET malware framework consisting of a number of modules concentrating on totally different cloud companies. The title CloudScout originated from the PDB paths of the modules obtained:
- E:projectgit_newMProjectsCodeCloudScoutGoogleDriverCGDobjDebugCGD.pdb
- E:projectgit_newMProjectsCodeCloudScoutGmailCGMobjDebugCGM.pdb
- E:projectgit_newMProjectsCodeCloudScoutOutlookCOLobjDebugCOL.pdb
We additionally discovered point out of seven different modules within the framework (see the part CommonUtilities: The heart of CloudScout); on the time of writing, we now have not but noticed them deployed on compromised machines, hinting that the attackers deploy them selectively. Altogether, the entire listing of CloudScout modules is:
- CGD
- CGM
- COL
- CTW
- CFB
- GMQ
- MEXC
- CEXC
- CZI
- CNE
Primarily based on the naming conference (e.g., the module concentrating on Google Drive known as CGD, the one concentrating on Gmail CGM, and the one concentrating on Outlook COL), we infer that CTW and CFB presumably goal Twitter and Fb. Nonetheless, the aim of different modules stays undetermined.
Improvement timing
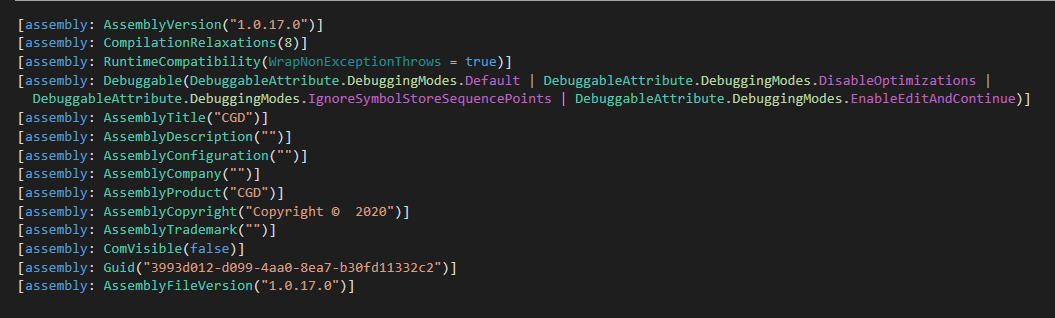
The AssemblyCopyright area’s worth, Copyright © 2020, within the .NET manifest of CloudScout modules, as seen in Determine 2, means that the CloudScout toolset might need been developed round 2020. Despite the fact that the legitimacy of the .NET manifest is questionable, it’s constant throughout all of the samples that we discovered. As well as, totally different variations said within the AssemblyVersion of CGD and CGM replicate the adjustments added to their code base.
We additionally discovered totally different variations of the embedded inner custom-made library package deal CommonUtilities. Desk 1 reveals totally different variations of CGD, CGM, and COL containing totally different variations of CommonUtilities.
Desk 1. Variations of CloudScout modules
| Module | Model | SHA-1 | CommonUtilities model |
| CGD | 1.0.11 | 67028AEB095189FDF18B2D7B775B62366EF224A9 | 1.0.08 |
| 1.0.14 | B3556D1052BF5432D39A6068CCF00D8C318AF146 | 1.0.10 | |
| 1.0.17 | 84F6B9F13CDCD8D9D15D5820536BC878CD89B3C8 | 1.0.11 | |
| CGM | 1.0.11 | 4A5BCDAAC0BC315EDD00BB1FCCD1322737BCBEEB | 1.0.08 |
| 1.0.13 | C058F9FE91293040C8B0908D3DAFC80F89D2E38B | 1.0.10 | |
| 1.0.14 | 621E2B50A979D77BA3F271FAB94326CCCBC009B4 | 1.0.11 | |
| COL | 1.0.10 | 93C1C8AD2AF64D0E4C132F067D369ECBEBAE00B7 | 1.0.08 |
Assuming that the .NET manifest is correct, in 2020 alone, we noticed three new toolsets from Evasive Panda. The opposite two situations are the primary look of Nightdoor and a brand new UDP variant of MgBot (succeeding the UDT variant).
Previous canine, new tips
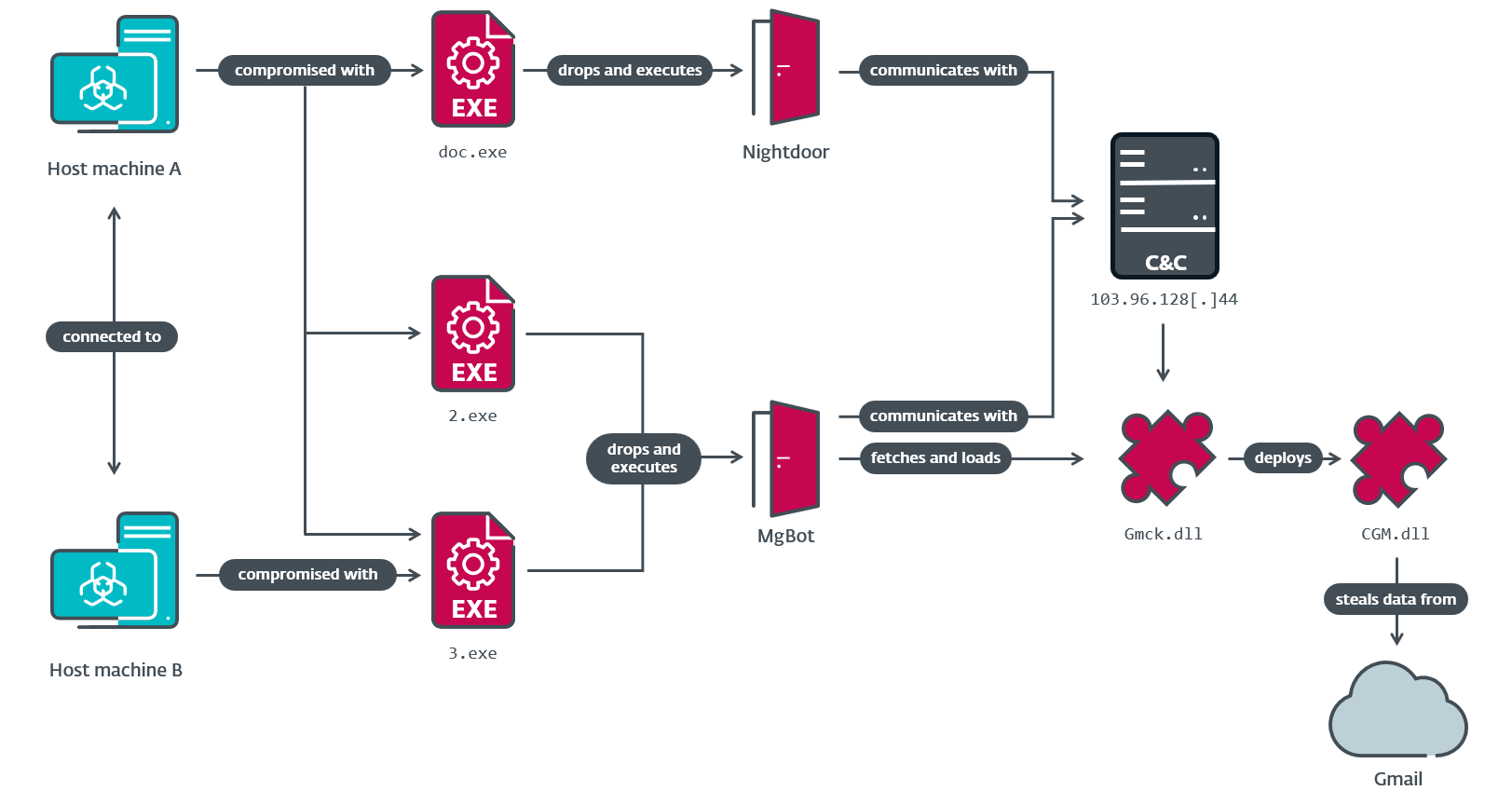
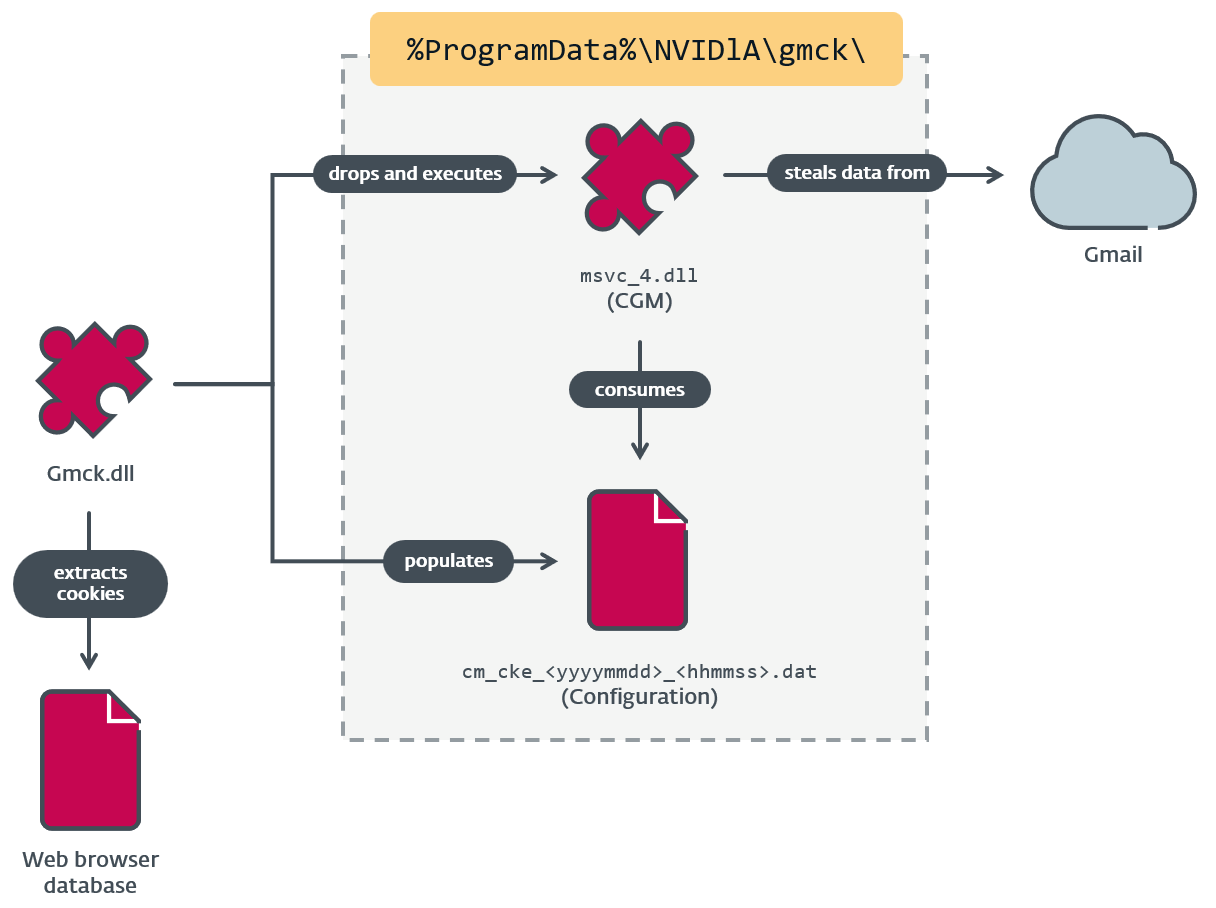
From a standard RC4 encryption key shared by the three modules, we carried out a retrohunt and found that CGM was deployed by an MgBot plugin referred to as Gmck.dll, which was programmed in C++. The plugin was detected in an incident in 2022 the place two machines from the aforementioned non secular establishment in Taiwan had been compromised by Evasive Panda. In that incident (illustrated in Determine 3), MgBot put in the CGM module, which in flip accessed the sufferer’s Gmail account to obtain emails and private data.
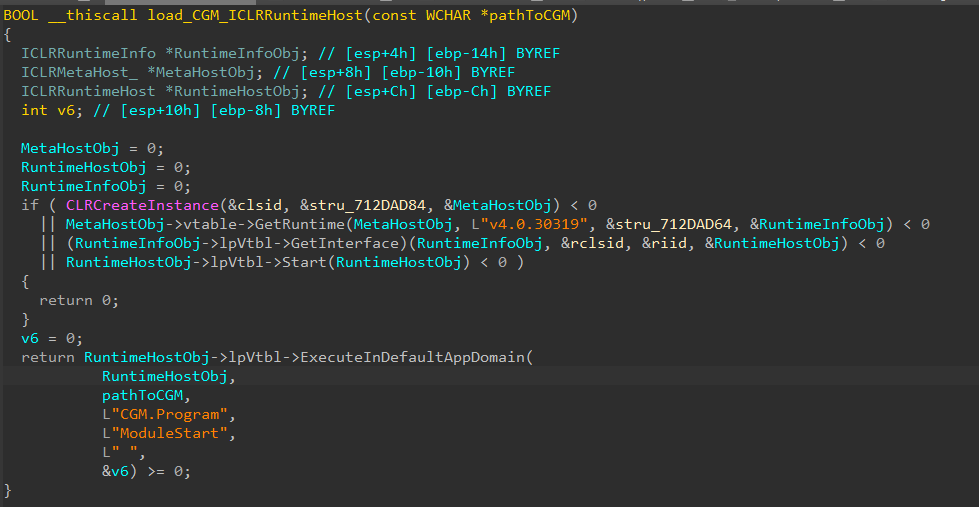
Gmck.dll (which we are going to consult with as Gmck) carries the .NET module CGM inside its binary. So as to execute CGM, Gmck first drops the module to disk at a hardcoded path, then begins the frequent language runtime (CLR) utilizing ICLRMetaHost and ICLRRuntimeHost. Lastly, it calls ExecuteInDefaultAppDomain with a reference to CGM’s entry level operate (ModuleStart), as seen in Determine 4.
In response to our telemetry, CGD and COL modules are additionally written to the identical staging folder, as proven in Desk 2.
Desk 2. Paths the place CloudScout modules are deployed
| MgBot plugin | Deployment path | CloudScout module |
| Gmck.dll | %ProgramDatapercentNVIDlAgmckmsvc_4.dll | CGM |
| N/A | %ProgramDatapercentNVIDlAolckmsvc_4.dll | COL |
| N/A | %ProgramDatapercentNVIDlAdankdhmsvc_4.dll | CGD |
The staging folder NVIDlA is purposely misspelled utilizing a easy homograph: it’s all in uppercase letters besides that the letter after the D is a lowercase letter el. The subfolders (as highlighted) appear to be named after the MgBot plugins. Sadly, we now have been unable to acquire the olck and dankdh plugins.
After the CGM module is efficiently deployed, the Gmck plugin wants to offer browser cookies to CGM within the type of a configuration file. Gmck extracts these cookies from internet browser database recordsdata listed in Desk 3. With the discharge of App-Bound Encryption in Chrome 127 and Edge 128, Gmck is now not in a position to decrypt Cookies database recordsdata from Chrome and Edge.
Desk 3. Database recordsdata from which Gmck extracts cookies
| Focused browser | Database recordsdata |
| Chrome | %localappdatapercentGoogleChromeUser DataLocal State %localappdatapercentGoogleChromeUser Knowledge<username>NetworkCookies |
| Edge | %localappdatapercentMicrosoftEdgeUser DataLocal State %localappdatapercentMicrosoftEdgeUser Knowledge<username>NetworkCookies |
| Firefox | %AppDatapercentMozillaFirefoxprofiles.ini %AppDatapercentMozillaFirefox<profile_name>cookies.sqlite |
The configuration file should have a .dat extension and be RC4 encrypted utilizing the important thing 0dda5a8d-e4c2-477d-85df-fcb611a62ffe to be able to be acknowledged by CGM. This RC4 secret is utilized by all three CloudScout modules to decrypt the configuration recordsdata, which implies the MgBot plugins should additionally use this key for encryption.
Determine 5 summarizes the connection between Gmck and CGM.
Configuration
The configuration file cm_cke_<yyyyymmdd>_<hhmmss>.dat in Determine 5 is supplied by the MgBot plugin after it extracts cookies from an internet browser’s database. The CloudScout module obtains a brand new configuration by repeatedly monitoring its working listing, in search of recordsdata with .dat extensions. For every .dat file that it finds, the CloudScout module spawns a brand new thread to deal with the file, which implies it could possibly deal with a number of configuration recordsdata on the identical time. The newly spawned thread handles a full assortment cycle, from parsing the configuration to downloading all of the focused information. On the finish of the cycle, the configuration file is faraway from disk to stop unintentionally repeating the identical cycle.
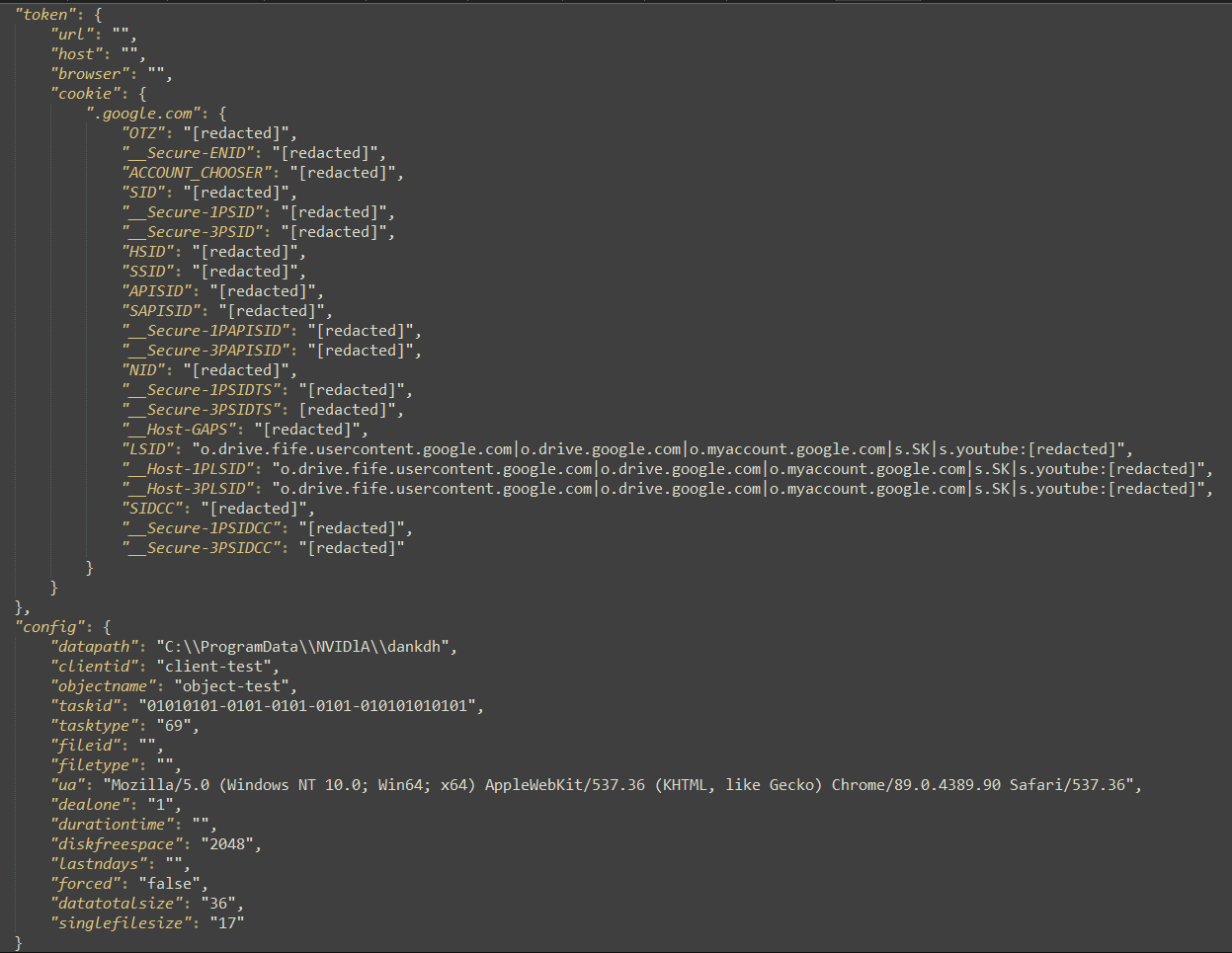
The configuration file is in JSON format. It incorporates two major information buildings: token and config. The token construction incorporates the cookies organized by area title. And config incorporates settings for downloading and staging the collected information for exfiltration, in addition to for protecting this system operating or exiting after a profitable cycle (dealone area). An instance of a configuration file is included in Determine 6.
CommonUtilities: The center of CloudScout
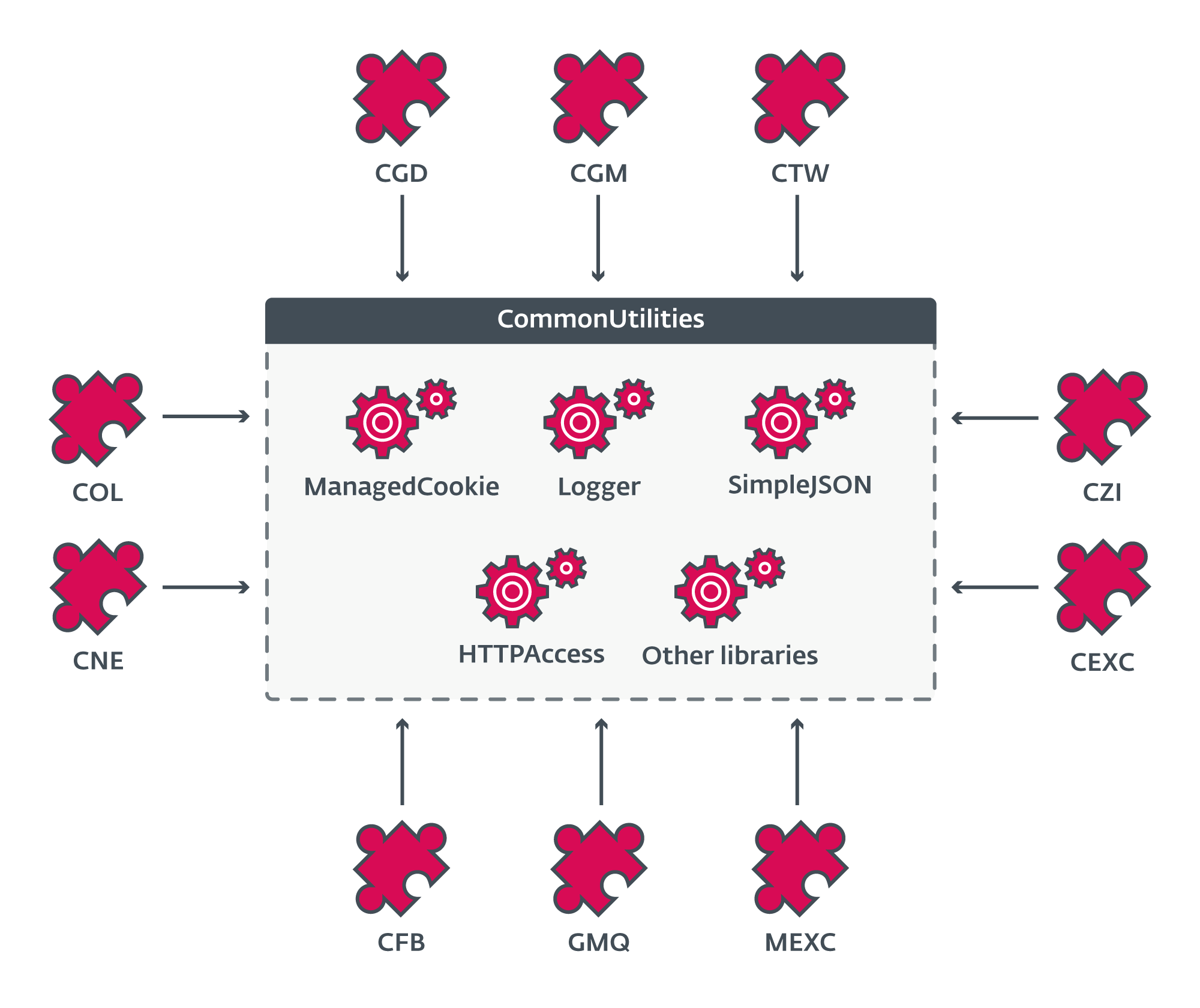
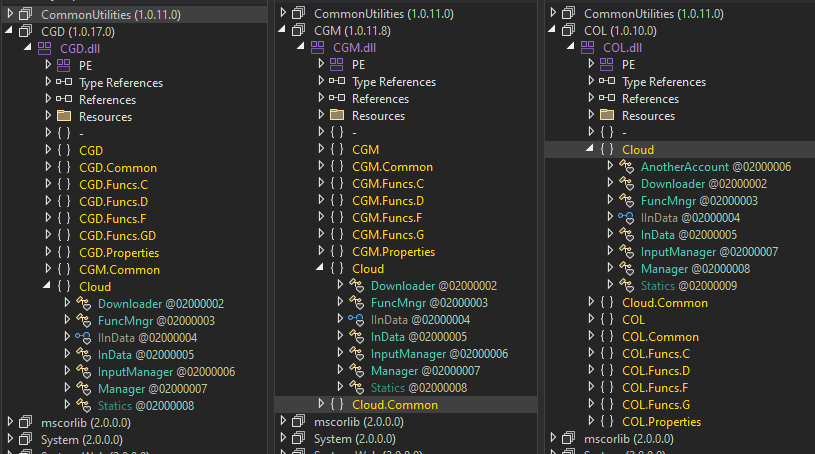
On the coronary heart of CloudScout is the CommonUtilities package deal, which gives all essential low-level libraries for the modules to run, as illustrated in Determine 7. This package deal is saved within the assets part of CloudScout modules and is loaded firstly of the ModuleStart operate.
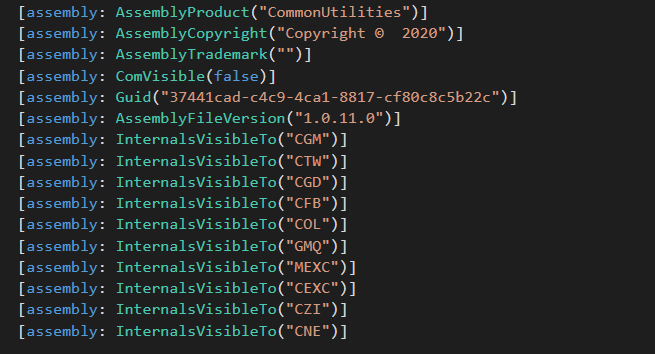
As seen in Determine 8, the .NET manifest of CommonUtilities reveals all of its shopper modules.
CommonUtilities incorporates fairly a number of custom-implemented libraries regardless of the considerable availability of comparable open-source libraries on-line. These {custom} libraries give the builders extra flexibility and management over the internal workings of their implant, in comparison with open-source options. Additionally they manifest sure unpredictable behaviors that compelled us to dig deep into the code to grasp. Examples of those {custom} libraries are HTTPAccess and ManagedCookie.
HTTPAccess gives essential features to deal with all of the HTTP communications of CloudScout modules. It has the aptitude of modifying HTTP headers, as proven in Determine 9.
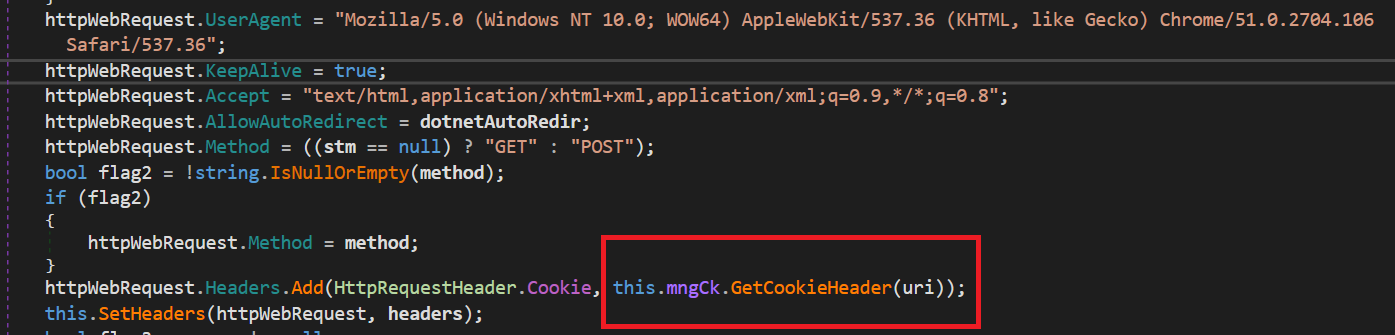
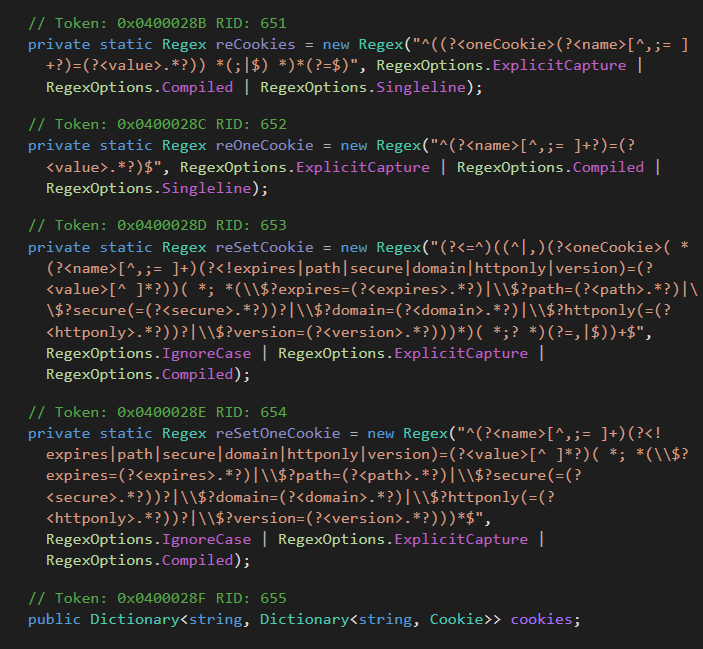
As highlighted on this code snippet, the this.mngCk object, an occasion of the ManagedCookie class, is used to combine cookies into the crafted HTTP headers. Because the title suggests, ManagedCookie gives features to handle cookies for internet requests between CloudScout and focused cloud companies. What makes this class particular is its complete listing of cookie parsers able to turning most cookies into default .NET cookie objects. Determine 10 reveals the totally different regexes created to match numerous mixtures of attribute-value pairs in cookies.
The body of CloudScout
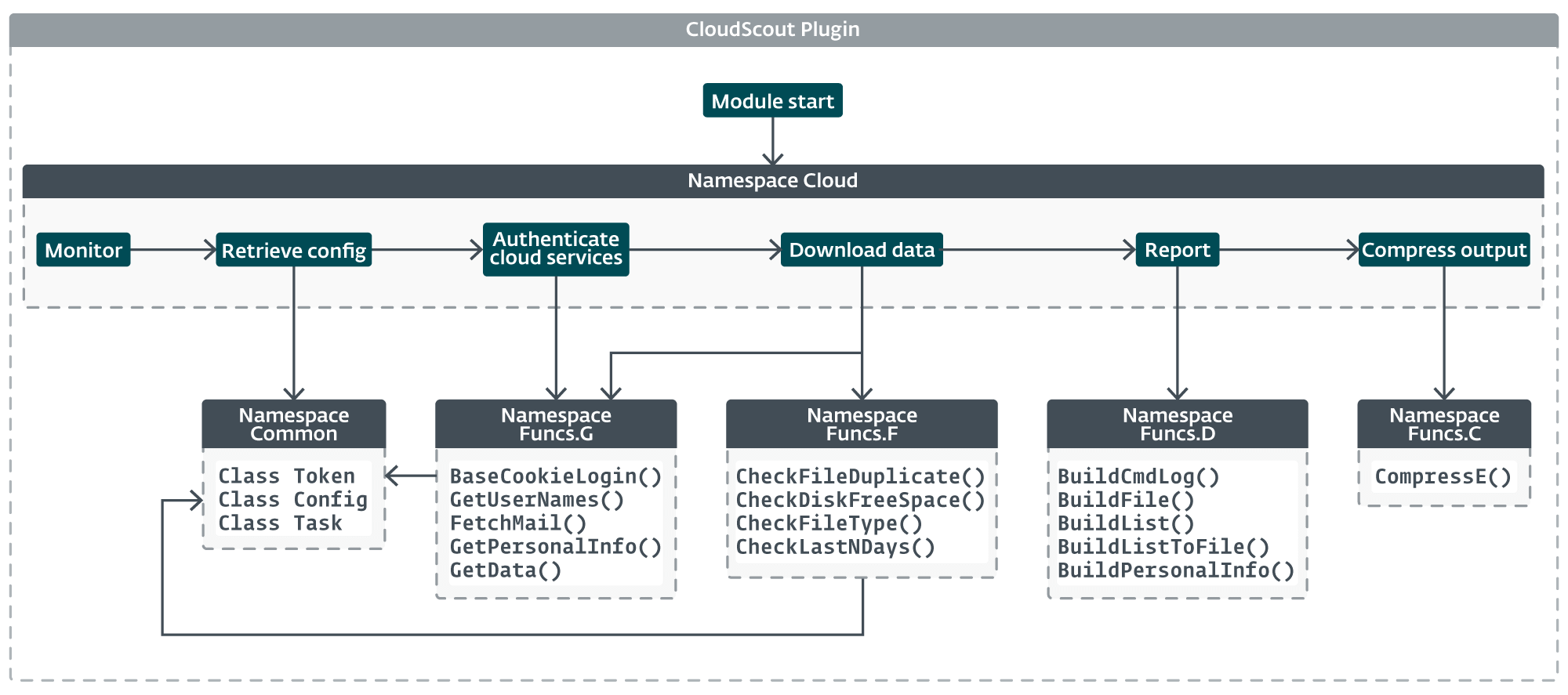
All CloudScout modules share a uniform structure, as proven in Determine 11. The core performance of the module is within the Cloud namespace, which is almost similar in every module. The implementation solely diverges in features associated to authentication and information retrieval, the place every module must generate particular internet requests or to parse sure internet responses based on the cloud service it targets.
The streamlined design of CloudScout and the core logic of the Cloud namespace is illustrated in Determine 12.
Authentication
Cookies normally usually are not very properly documented by internet platforms. Authentication cookies are likely to have quick lifespans and are often up to date because the consumer interacts with the platform through an internet browser. Nonetheless, so long as the classes are nonetheless legitimate, the cookies listed in Desk 4 could be abused by CloudScout to entry and obtain precious information from cloud companies.
Desk 4. Authentication cookies dealt with by the CloudScout modules
| Service | Area | Required cookies |
| Google Drive | drive.google.com accounts.google.com |
OSID, HSID, SID, SSID, APISID, SAPISID, LSID |
| Gmail | mail.google.com accounts.google.com |
|
| Outlook | outlook.reside.com login.reside.com |
X-OWA-CANARY, RPSSecAuth, ClientId |
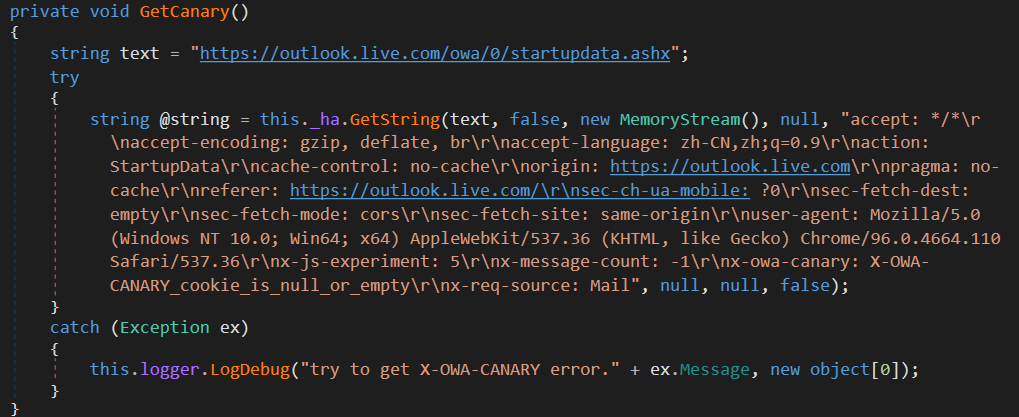
X-OWA-CANARY is a safety cookie utilized by Microsoft Outlook Net Entry (OWA) to stop cross-site request forgery assaults. It’s assigned firstly of every session when the consumer is authenticated. CloudScout’s COL module implements a mechanism to retrieve this cookie when it isn’t out there, by establishing a brand new session utilizing the RPSSecAuth and ClientId cookies to reauthenticate, as proven in Determine 13.
Knowledge retrieval
After authentication, the CloudScout modules browse the compromised cloud service accounts in a fashion much like how a daily consumer would with an internet browser. To attain this, every CloudScout module is provided with a set of hardcoded internet requests to carry out, together with advanced HTML parsers, which determine and extract the information of curiosity from the online responses.
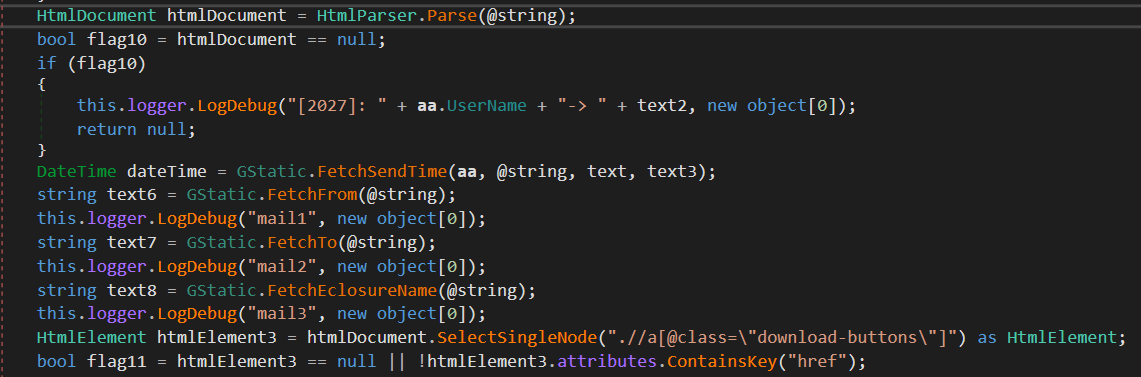
For instance, the CGM and COL modules are keen on mail folder listings and e mail messages, concentrating on Gmail and Outlook, respectively. Determine 14 reveals the steps that CGM performs to extract e mail headers, e mail our bodies, and attachments from the HTML content material served by the Gmail internet server.
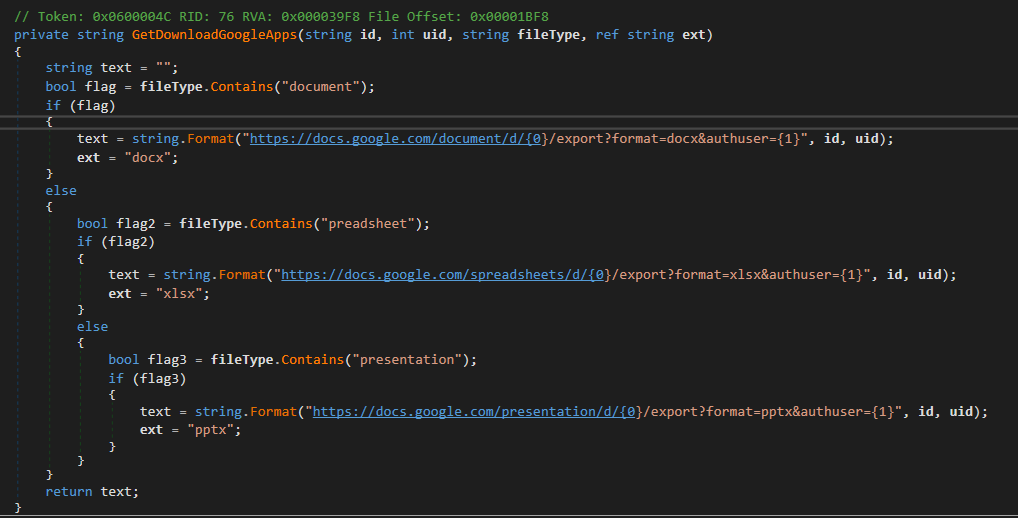
However, CGD is keen on consumer data from Google Drive; a full listing hierarchy; and recordsdata with extensions .doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx, .ppt, .pptx, .pdf, and .txt. Determine 15 is the code snippet from CGD to generate a obtain URL for a doc.
The module appends a {custom} header to every downloaded merchandise, whether or not it’s a file or an e mail. This tradition header consists of metadata of the merchandise akin to shopper ID (assigned by the malware), e mail topic, or filename, and the username of the cloud service (Desk 5). The added header most definitely permits stolen information to be processed at scale, by automated techniques, for fast indexing or to carry out evaluation.
Desk 5. Customized headers for downloaded e mail and recordsdata
| Mail header | File header |
| tasktype: taskid: clientid: objectname: mailid: username: topic:=?utf-8?b?<base64_encoded_data>?= froms:=?utf-8?b?<base64_encoded_data>?= tos:=?utf-8?b?<base64_encoded_data>?= kind: sourceflag: Outlook filepath: mailcountry: attachment: mailboxtype:gmail folder:=?utf-8?b? <base64_encoded_data>?= time: <yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss> captime: <yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss> |
tasktype: taskid: clientid: objectname: username: skydrivetype:googledrive path:=?utf-8?b? ?<base64_encoded_data>?= supply:googledrive filename:=?utf-8?b? ?<base64_encoded_data>?= key: filetime: <yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss> measurement: kind:googledrive captime: <yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss> |
After including the header, every merchandise is encrypted utilizing the identical RC4 key as used for the configuration file and saved with the filename <pseudorandom_GUID>.<{custom}_extension>, the place <custom_extension> signifies the kind of stolen information, as listed in Desk 6.
Desk 6. Filename extension for every information class
| Knowledge class | CGD | CGM or COL |
| Private data | .pc_plug_googledrive_profile | N/A |
| Electronic mail | N/A | .pc_plug_gmck_email |
| Listing itemizing | .pc_plug_googledrive_filelist | .pc_plug_gmck_email_list |
| File | .pc_plug_googledrive_file | N/A |
Subsequent, all objects are compressed right into a ZIP archive named <pseudorandom_GUID>.hxkz_zip and positioned in a listing for exfiltration as specified by the datapath area of the configuration. This archive can later be exfiltrated by both MgBot or Nightdoor. Within the last step, the CloudScout modules do a full cleanup, eradicating all artifacts generated through the assortment cycle besides the recordsdata to be exfiltrated, earlier than checking the dealone flag to both exit or to proceed and look forward to a brand new configuration file to start out a brand new assortment cycle.
Conclusion
CloudScout is a .NET toolset utilized by Evasive Panda to steal information saved in cloud companies. It’s carried out as an extension to MgBot and makes use of the pass-the-cookie approach to hijack authenticated classes from internet browsers.
On this blogpost, we now have highlighted the skilled design behind the CloudScout framework to show Evasive Panda’s technical capabilities and the essential roles that cloud-stored paperwork, consumer profiles, and e mail play in its espionage operations.
For any inquiries about our analysis printed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.ESET Analysis gives personal APT intelligence reviews and information feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Threat Intelligence web page.
IoCs
A complete listing of indicators of compromise (IoCs) and samples could be present in our GitHub repository.
Information
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| C70C3750AC6B9D7B033A |
pmsrvd.dll | Win32/Agent.AELQ | MgBot loader. |
| 812124B84C5EA455F714 |
pmsrvd.dll | Win32/Agent.AELQ | MgBot loader. |
| AD6C84859D413D627AC5 |
3.exe | Win32/Agent.ADJV | MgBot dropper. |
| 3DD958CA6EB7E8F0A061 |
1.exe | Win32/Agent.ADJV | MgBot dropper. |
| 547BD65EEE05D744E075 |
doc.exe | Win32/Agent.AFXX | Nightdoor dropper. |
| 348730018E0A5554F0F0 |
DJCU.dll | Win32/Nightdoor.A | Nightdoor loader. |
| 9B6A473820A72111C1A3 |
CommonUtilities.dll | MSIL/Agent.UEK | CloudScout inner library package deal model 1.0.0. |
| 621E2B50A979D77BA3F2 |
CGM.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout Gmail stealer model 1.0.14. |
| C058F9FE91293040C8B0 |
CGM.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout Gmail stealer model 1.0.13. |
| 4A5BCDAAC0BC315EDD00 |
CGM.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout Gmail stealer model 1.0.18. |
| 67028AEB095189FDF18B |
CGD.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout Google Drive stealer model 1.0.11. |
| B3556D1052BF5432D39A |
CGD.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout Google Drive stealer model 1.0.14. |
| 84F6B9F13CDCD8D9D15D |
CGD.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout Google Drive stealer model 1.0.17. |
| 93C1C8AD2AF64D0E4C13 |
COL.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout Outlook Net Entry stealer model 1.0.10. |
| 8EAA213AE4D482938C5A |
CommonUtilities.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout inner library package deal model 1.0.8. |
| A1CA41FDB61F03659168 |
CommonUtilities.dll | MSIL/CloudScout.A | CloudScout inner library package deal model 1.0.11. |
Community
| IP | Area | Internet hosting supplier | First seen | Particulars |
| 103.96.128[.]44 | N/A | IRT-WUZHOUHULIAN-HK | 2022-05-26 | MgBot and Nightdoor C&C server. |
MITRE ATT&CK strategies
This desk was constructed utilizing version 15 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
| Tactic | ID | Identify | Description |
| Useful resource Improvement | T1583.004 | Purchase Infrastructure: Server | Evasive Panda acquired servers for the C&C infrastructure of MgBot and Nightdoor. |
| T1587.001 | Develop Capabilities: Malware | Evasive Panda developed {custom} implants akin to MgBot, CloudScout, and Nightdoor. | |
| Execution | T1569.002 | System Companies: Service Execution | MgBot is executed as a Home windows service. |
| T1106 | Execution via API | The MgBot installer makes use of Home windows APIs to create processes. Gmck makes use of ExecuteInDefaultAppDomain to execute CGM within the CLR. | |
| Persistence | T1543.003 | Create or Modify System Course of: Home windows Service | MgBot replaces the prevailing Utility Administration service DLL path with its personal. |
| Privilege Escalation | T1548.002 | Abuse Elevation Management Mechanism: Bypass Consumer Entry Management | MgBot performs UAC bypass. |
| Protection Evasion | T1140 | Deobfuscate/Decode Information or Info | Gmck decrypts Chrome, Edge, and Firefox internet browser databases to extract cookies. |
| T1112 | Modify Registry | MgBot modifies the registry for persistence. | |
| T1027 | Obfuscated Information or Info | Gmck obfuscates the configuration that incorporates cookies. | |
| T1550.004 | Use Alternate Authentication Materials: Net Session Cookie | CloudScout makes use of stolen cookies to entry cloud assets. | |
| T1036.005 | Masquerading: Match Authentic Identify or Location | CloudScout modules are put in to %ProgramDatapercentNVIDlA to imitate an NVIDIA listing. | |
| Credential Entry | T1539 | Steal Net Session Cookie | Gmck steals cookies. |
| Discovery | T1082 | System Info Discovery | MgBot collects system data. |
| Assortment | T1560.001 | Archive Collected Knowledge: Archive through Utility | CloudScout modules use SharpZipLib to compress information earlier than exfiltration. |
| T1530 | Knowledge from Cloud Storage Object | CGD downloads recordsdata saved on Google Drive. | |
| T1114.002 | Electronic mail Assortment: Distant Electronic mail Assortment | CGM and COL entry and acquire emails from Gmail and Outlook Net Entry, respectively. | |
| Command and Management | T1095 | Non-Utility Layer Protocol | MgBot communicates with its C&C through UDP. |
| Exfiltration | T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | MgBot exfiltrates collected information to its C&C. |




