In July 2024, ESET Analysis seen suspicious exercise on the system of a commerce group in the US that operates within the monetary sector. Whereas serving to the affected entity remediate the compromise, we made an surprising discovery within the sufferer’s community: malicious instruments belonging to FamousSparrow, a China-aligned APT group. There had been no publicly documented FamousSparrow exercise since 2022, so the group was considered inactive. Not solely was FamousSparrow nonetheless lively throughout this era, it should have additionally been onerous at work growing its toolset, because the compromised community revealed not one, however two beforehand undocumented variations of SparrowDoor, FamousSparrow’s flagship backdoor.
Each of those variations of SparrowDoor represent marked progress over earlier ones, particularly by way of code high quality and structure. One among them resembles the backdoor that researchers at Pattern Micro known as CrowDoor and attributed to the Earth Estries APT group in November 2024. The opposite is modular and considerably completely different from all earlier variations. This marketing campaign can be the primary documented time FamousSparrow used ShadowPad, a privately sold backdoor, identified to solely be provided to China-aligned risk actors.
We additional found that, as a part of this marketing campaign, the risk actor managed to breach a analysis institute in Mexico simply a few days previous to the compromise within the US.
Whereas organising monitoring primarily based on what we found in these assaults, we uncovered further exercise by the group between 2022 and 2024, which we’re nonetheless investigating. Amongst others, it focused a governmental establishment in Honduras.
This blogpost gives an outline of the toolset used within the July 2024 marketing campaign, specializing in the undocumented variations of the SparrowDoor backdoor that we found on the US sufferer.
Key factors of this blogpost:
- ESET researchers found that FamousSparrow compromised a commerce group for the monetary sector in the US and a analysis institute in Mexico.
- FamousSparrow deployed two beforehand undocumented variations of the SparrowDoor backdoor, one among them modular.
- Each variations represent appreciable progress over earlier ones and implement parallelization of instructions.
- The APT group was additionally noticed utilizing the ShadowPad backdoor for the primary time.
- We focus on Microsoft Risk Intelligence’s attribution claims linking FamousSparrow to Salt Storm.
FamousSparrow is a cyberespionage group with ties to China, lively since at the least 2019. We first publicly documented the group in a 2021 blogpost once we noticed it exploiting the ProxyLogon vulnerability. The group was initially identified for concentrating on resorts all over the world, however has additionally focused governments, worldwide organizations, engineering firms, and legislation corporations. FamousSparrow is the one identified consumer of the SparrowDoor backdoor.
Despite the fact that FamousSparrow appeared inactive on the time of our discovery, we attribute this exercise to the group with excessive confidence. The deployed payloads are new variations of SparrowDoor, a backdoor that seems to be unique to this group. Whereas these new variations exhibit important upgrades in code high quality and structure, they will nonetheless be traced again on to earlier, publicly documented variations. The loaders utilized in these assaults additionally current substantial code overlaps with samples beforehand attributed to FamousSparrow. Notably, they use the identical reflective loader shellcode because the libhost.dll loader pattern described in a report from February 2022 revealed by the UK Nationwide Cyber Safety Centre (NCSC). Its configuration additionally shares the identical particular format, aside from the encryption key which is as a substitute hardcoded within the loader and backdoor. XOR encryption has additionally been changed with RC4.
Moreover, C&C server communications use a format similar to that utilized in earlier SparrowDoor variations.
In 2021, Kaspersky researchers wrote a couple of risk actor they observe as GhostEmperor. Regardless of some infrastructure overlap with FamousSparrow, we observe them as separate teams. In August 2023, Pattern Micro noted that some FamousSparrow TTPs overlap with these of Earth Estries. We’ve got additionally noticed code overlaps between SparrowDoor and that group’s HemiGate. These are mentioned in additional element within the Plugins part. We imagine that the 2 teams overlap at the least partially, however we don’t have sufficient knowledge to completely assess the character and extent of the hyperlink between the 2 teams.
FamousSparrow and Salt Storm
Earlier than we dive into the evaluation of FamousSparrow’s toolset, we wish to focus on our place on the hyperlinks between FamousSparrow and Salt Storm made by Microsoft Risk Intelligence.
In September 2024, the Wall Road Journal revealed an article (the article is behind a paywall) reporting that web service suppliers in the US had been compromised by a risk actor named Salt Storm. The article relays claims by Microsoft that this risk actor is identical as FamousSparrow and GhostEmperor. It’s the first public report that conflates the latter two teams. Nonetheless, as we already acknowledged, we see GhostEmperor and FamousSparrow as two distinct teams. There are few overlaps between the 2 however many discrepancies. Each used 27.102.113[.]240 as a obtain server in 2021. Each teams had been additionally early exploiters of the ProxyLogon vulnerability (CVE-2021-26855) and have used a few of the identical publicly obtainable instruments. Nonetheless, moreover these publicly obtainable instruments, every risk actor has its personal customized toolset.
Since that preliminary publication, researchers at Pattern Micro have added Earth Estries to the listing of teams which can be linked to Salt Storm. As of this writing, Microsoft, who created the Salt Storm cluster, has not revealed any technical indicators or particulars about TTPs utilized by the risk actor, nor offered a proof for this attribution. To keep away from additional muddying the waters, we are going to hold monitoring the cluster of exercise we see as straight linked to SparrowDoor as FamousSparrow till now we have info essential to reliably assess these attribution claims.
Primarily based on our knowledge and evaluation of the publicly obtainable reviews, FamousSparrow seems to be its personal distinct cluster with unfastened hyperlinks to the others talked about on this part. We imagine these hyperlinks are higher defined by positing the existence of a shared third occasion, comparable to a digital quartermaster, than by conflating all of those disparate clusters of exercise into one.
Technical Evaluation
So as to achieve preliminary entry to the affected community, FamousSparrow deployed a webshell on an IIS server. Whereas we had been unable to find out the precise exploit used to deploy the webshells, each victims had been operating outdated variations of Home windows Server and Microsoft Trade, for which there are a number of publicly obtainable exploits.
As for the toolset used within the marketing campaign, the risk actor employed a mixture of customized instruments and malware together with these shared by China-aligned APT teams, in addition to from publicly obtainable sources. The ultimate payloads had been SparrowDoor and ShadowPad. Determine 1 gives an outline of the compromise chain deployed within the assaults.
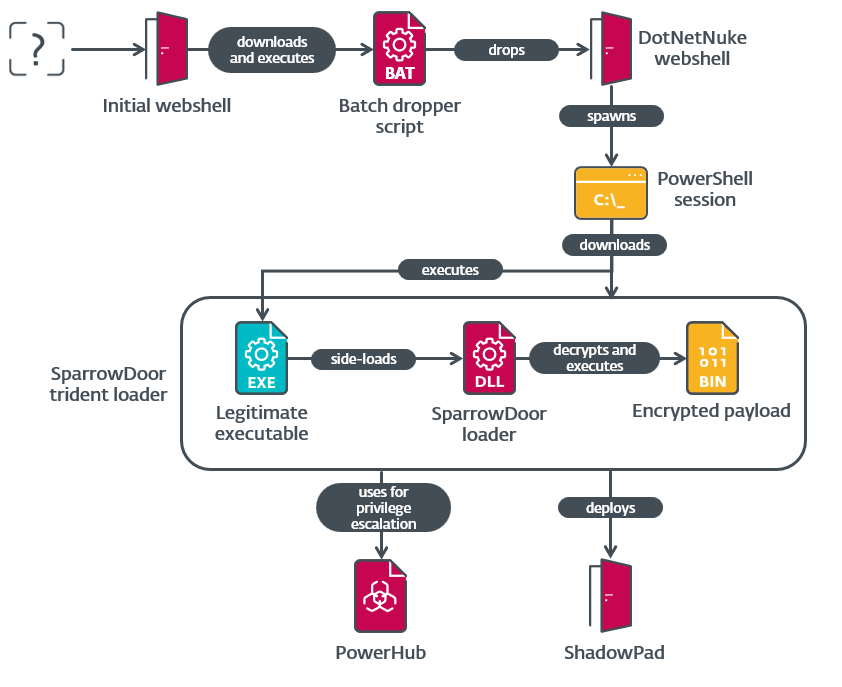
The risk actor initially downloaded a batch script over HTTP from a obtain server, 43.254.216[.]195. This script incorporates a base64-encoded .NET webshell that it writes to C:userspublics.txt. It then decodes it utilizing certutil.exe and saves the decoded output to C:userspublics.ashx. An ASHX module is a kind of HTTP handler for ASP.NET. Though much like ASPX modules, ASHX modules don’t embody any consumer interface parts. The script then walks by way of drives C: to I:, and P:, to search out the set up listing of DotNetNuke; it then copies the ASHX webshell to <DotNetNuke_directory>DesktopModulesDotNetNuke.ashx.
The webshell itself is pretty generic and doesn’t use something particular to DotNetNuke. All the info it receives, and returns, is AES encrypted with the hardcoded key e2c99096bcecd1b5. On first request, it expects a .NET PE file. This executable file is loaded into reminiscence and saved in a session variable. On subsequent requests, an occasion of the LY class contained inside that .NET meeting is created and the info acquired is handed to its Equals methodology. We didn’t gather any payload despatched to this webshell, nevertheless it’s apparent that the Equals method doesn’t observe the everyday contract.
Within the instances we noticed, this was used to spawn an interactive distant PowerShell session. As soon as this session was established, attackers used official Home windows instruments to acquire details about the host and the Lively Listing domains to which it was joined. They then downloaded PowerHub, an open-source post-exploitation framework, from an attacker-controlled server and used the BadPotato privilege-escalation method to achieve SYSTEM privileges. This exploit will not be current within the framework, however it seems that the group added the open-source Invoke-BadPotato module to its deployment of PowerHub. Lastly, the attacker used PowerShell’s built-in Invoke-WebRequest to obtain three recordsdata from the identical server that comprise SparrowDoor’s trident loader.
In a course of similar to the one described in 2022 by the UK NCSC, the aforementioned recordsdata use a trident loading scheme to execute SparrowDoor. On this occasion, the executable used for DLL side-loading is a official model of K7AntiVirus Messenger Scanner named K7AVMScn.exe, whereas the malicious DLL and encrypted payload recordsdata are named K7AVWScn.dll and K7AVWScn.doc, respectively. The payload file is encrypted utilizing an RC4 key that’s hardcoded in each the loader and the ensuing decrypted payload, however which varies throughout samples.
The decrypted payload consists of a customized configuration and reflective loader shellcode virtually similar to that described by the UK NCSC, with the one distinction being that the primary area, which contained the four-byte XOR key, has been eliminated. The final 202 bytes of the file are encrypted individually, however utilizing the identical RC4 key, and include the C&C server configuration.
SparrowDoor
As acknowledged, we noticed two new variations of SparrowDoor utilized in these assaults. The primary one is similar to what was known as CrowDoor by researchers at Pattern Micro, in an article revealed in November 2024 about Earth Estries. This malware was first documented by researchers at ITOCHU and Macnica in a presentation at VirusBulletin in 2023. From our perspective, these are a part of the continued growth effort on SparrowDoor somewhat than a distinct household. We are able to observe the evolution from the primary model we described in 2021, by way of those known as CrowDoor, to the modular model we analyze within the later a part of this blogpost.
Each variations of SparrowDoor used on this marketing campaign represent onsiderable advances in code high quality and structure in comparison with older ones. Essentially the most important change is the parallelization of time-consuming instructions, comparable to file I/O and the interactive shell. This permits the backdoor to proceed dealing with new instructions whereas these duties are carried out. We are going to clarify the process later within the blogpost once we focus on the instructions intimately.
Similar to in earlier variations, the conduct of the backdoor varies relying on the command line argument handed to it. These are listed in Desk 1.
Desk 1. Command line arguments for SparrowDoor
| Argument | Habits |
| No argument | Set up persistence. |
| 11 | Process hollowing of colorcpl.exe. |
| 22 | Primary backdoor operation. |
When executed with none arguments, the malware establishes persistence. It first tries to take action by making a service named K7Soft that’s set to run robotically on startup. If this fails, a registry Run key with the identical title is used as a substitute. In each instances, the persistence mechanism is ready to execute the backdoor with a command line argument of 11. It is usually launched instantly with that very same argument utilizing the StartServiceA or ShellExecuteA API.
When executed with the argument 11, the backdoor launches the Home windows coloration administration instrument (colorcpl.exe) with a command line argument of 22 and injects its loader into the newly created course of.
It’s only when the command line argument is ready to 22 that the backdoor truly executes its principal payload.
After SparrowDoor is executed on this backdoor mode, it terminates, in a roundabout method, every other already operating situations. The backdoor makes use of the K32EnumProcesses API to iterate by way of the method IDs (PIDs) of all operating processes and tries to create a mutex named GlobalID(<PID>). PIDs of 15 or much less are skipped, probably as a approach to exclude killing some important system processes. If the mutex already exists, the method is terminated. In any other case, the mutex is closed instantly. When SparrowDoor is completed iterating by way of the PIDs, it creates a brand new mutex utilizing the identical title format and its personal PID.
The backdoor then reads the final 202 bytes from the encrypted payload file and decrypts them utilizing the identical RC4 key utilized by the loader. The ensuing plaintext is the C&C server configuration, which consists of three pairs of addresses and ports, adopted by 4 numeric values that, respectively, signify the variety of days, hours, minutes, and seconds the backdoor ought to wait in any case configured C&C servers have been tried. That is associated to the performance we describe later whereas speaking concerning the command the backdoor makes use of for altering the C&C configuration.
After loading this configuration, the backdoor will attempt to connect with the primary server. Whether it is unable to attach or if the C&C server points a command that causes execution to exit the principle command loop, SparrowDoor will attempt to connect with the subsequent server, and so forth. As soon as the final server within the configuration has been tried, the backdoor will sleep for the outlined time (six minutes within the pattern we analyzed), reload the configuration, after which repeat the method. Word that, throughout this time, SparrowDoor doesn’t reply to instructions. Nonetheless, the parallelized instructions that had been already operating will hold doing so till they full, encounter an error, or are terminated by the server.
The backdoor makes use of two classes to handle its connections: the summary CBaseSocket and its baby class CTcpSocket. These are primarily wrappers round Winsock TCP sockets. Whereas the category names are generic and observe the identical naming conference used within the Microsoft Foundation Class Library (MFC), the code they include seems to be customized.
SparrowDoor makes use of an integer worth as a sufferer or session identifier. That is despatched to the C&C server when it requests details about the host and every time a brand new socket is created. The worth is learn from the HKLMSoftwareCLASSESCLSIDID registry key, falling again to the identical path within the HKCU hive if there’s a problem. If it’s not current, the identifier is derived from the machine’s efficiency counter and written to the aforementioned registry key. Though the worth itself is benign, the usage of this nonstandard registry key presents a detection alternative. Certainly, the title of any registry key underneath SoftwareClassesCLSID ought to be a legitimate CLSID, that are represented as a GUID surrounded by curly brackets. Whereas it’s not essentially an indicator of maliciousness, the presence of keys with nonstandard names underneath CLSID is uncommon.
Instructions
The primary model of SparrowDoor used on this marketing campaign helps extra instructions, described in Desk 2, than beforehand documented variations. Whereas the command IDs are completely different from these used within the model analyzed by Trend Micro, the order and offset between IDs are the identical. We’ve got not had entry to that pattern, so we can not inform whether or not the extra instructions had been absent or just not publicly documented by the authors.
As beforehand talked about, a few of the instructions have been parallelized. When the backdoor receives one among these instructions, it creates a thread that initiates a brand new connection to the C&C server. The distinctive sufferer ID is then despatched over the brand new connection together with a command ID indicating the command that led to this new connection. This permits the C&C server to maintain observe of which connections are associated to the identical sufferer and what their functions are. Every of those threads can then deal with a particular set of subcommands. To restrict its complexity, Desk 2 doesn’t embody these subcommands; we are going to go over them individually.
Desk 2. Primary instructions carried out by SparrowDoor
| Command ID | Description | Obtained knowledge | Despatched knowledge |
| 0x32341122 | Preliminary connection. | No message | Empty |
| 0x32341123 | Ship host info. | Empty | · IP handle, · distinctive ID, · OS construct quantity, · OS main model quantity, · OS minor model quantity, · pc title, and · username. |
| 0x32341124 | Begin interactive shell session (parallel). | Empty | See the Interactive shell subsection. |
| 0x32341127 | Sleep, then transfer to the subsequent server within the configuration. | Minutes to sleep. | No response |
| 0x32341128 | Uninstall backdoor and clear up. | Empty | No response |
| 0x32341129 | Get present community configuration. | Empty | Community configuration construction. |
| 0x3234112A | Set community configuration. | Community configuration construction. | No response |
| 0x3234112B | Execute loader with the command line argument 11 and terminate the present course of. | Empty | No response |
| 0x3234112D | File I/O (parallel). | Operation ID. | See the File operations part. |
| 0x32341131 | Get details about related drives. | Empty | Array of 26 bytes representing the drive sort of all drives from A: to Z: as returned by GetDriveTypeW. |
| 0x32341132 | Record recordsdata. | Listing path. | File info, one response per file. See the File listing part. |
| 0x32341135 | Create listing. | Listing path. | No response |
| 0x32341136 | Transfer or rename file. | · Supply path size, · supply path, · vacation spot path size, and · vacation spot path. |
No response |
| 0x32341137 | Delete file. | File path. | No response |
| 0x32341138 | Begin proxy. | Empty | See the Proxy subsection. |
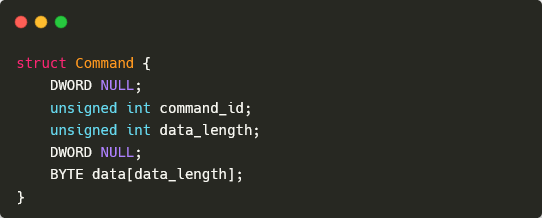
All communication between the malware and its C&C server makes use of the identical base packet format, outlined in Determine 2. The format of the info part will depend on the command despatched, and might be empty. Generally, responses use the ID of the command to which the backdoor is responding. There are, nevertheless, some exceptions; we are going to describe these when speaking concerning the related instructions intimately.
Interactive shell
Upon receiving the interactive shell command, SparrowDoor spawns a brand new thread and socket as beforehand described, and performs all the next actions inside this thread utilizing the brand new socket. First, the backdoor sends again an acknowledgment message with command ID 0x32341125 and the distinctive sufferer ID within the knowledge area. It then spawns a cmd.exe course of and makes use of a pair of threads and named pipes to relay instructions and their output between the C&C server and the shell. The named pipe .pipeid2<handle> is used to move instructions acquired from the C&C server to the shell and .pipeid1<handle> is used for the ensuing output on STDOUT and STDERR. In each situations, <handle> is the reminiscence handle, in decimal type, of the CTcpSocket occasion. These instructions use the ID 0x32341126 and the info is, respectively, the command line to be executed and the uncooked output. If the backdoor receives a message with the command ID set to every other worth, the interactive shell session is terminated.
Altering the C&C configuration
The C&C configuration is stored within the encrypted payload file. If the backdoor receives the command to alter this configuration (0x3234112A), the acquired construction is RC4 encrypted after which the final 202 bytes of the encrypted file are overwritten with the end result. Apparently, the configuration will not be robotically reloaded. As we defined beforehand, the configuration is just reloaded when all three configured servers have been tried. To forcibly reload the configuration, the server can challenge the 0x32341127 command or an invalid command, each of which is able to trigger SparrowDoor to exit the command loop and transfer to the subsequent server. The configuration can be reloaded if the backdoor is relaunched, comparable to through the use of the 0x3234112B command.
File operations
As with different instructions processed in parallel, every part right here is carried out in a brand new thread utilizing a brand new socket. SparrowDoor sends an acknowledgment message with the identical ID as the unique command. The physique of this message incorporates the distinctive ID of the sufferer and the operation ID despatched by the C&C server. This operation ID doesn’t seem to have any which means, and might be solely utilized by the server to hyperlink the connection to the file operation command if a number of such instructions are carried out in parallel. Command IDs 0x3234112E and 0x3234112F are used, respectively, for file reads and writes.
For a file learn, the message physique incorporates the beginning offset, the dimensions to be learn, and the trail to the file. If the requested learn goes previous the tip of the file, it causes an error and no response is distributed. In any other case, the malware reads the file in chunks of 4 kB, every of which is distributed within the physique of a message with the command ID 0x32341130.
The method is analogous for a file write. The preliminary message from the C&C incorporates the full dimension of the info to be written adopted by the goal file path. Apparently, the write is just carried out if this dimension is bigger than the present dimension of the goal file. The info is then despatched by the C&C server in chunks of 4 kB, utilizing the identical command ID of 0x32341130.
File itemizing
When the file itemizing command is acquired, the backdoor first sends again an acknowledgment message with the command ID 0x32341133. It then makes use of the FindFirstFileW and FindNextFileW API capabilities to iterate, non-recursively, by way of recordsdata within the goal listing. For every file, SparrowDoor sends one message, with the identical command ID because the listing file command (0x32341132) and the knowledge described in Determine 3. Word that, although the size of the filename isn’t specified straight, it may be obtained by subtracting the dimensions of the remainder of the fields (0x16) from the data_length worth within the header.
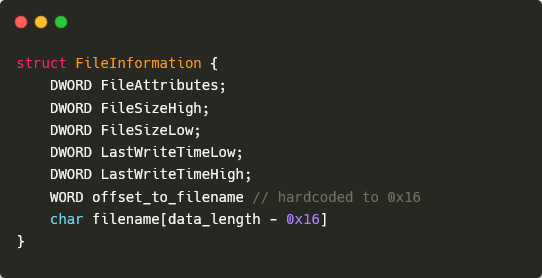
As soon as the iteration is completed, a message with command ID 0x32341134 and no knowledge is distributed to point that the file itemizing operation has accomplished efficiently.
Proxy
This performance permits the backdoor to behave as a TCP proxy between the C&C server and an arbitrary machine. As with different instructions processed in parallel, the next is completed in a brand new thread utilizing its personal socket. SparrowDoor sends an acknowledgment message with the identical ID as the unique command; the physique of this message incorporates the distinctive ID of the sufferer. Command ID 0x32341139 is then despatched by the server to really provoke the proxy. The proxy performance is achieved by creating two new sockets, one related to the C&C server and one other related to an handle and port offered by the server on that new connection. SparrowDoor then makes use of a pair of Winsock structures and events to maintain observe of incoming packets and relay them between the 2 events. The addition of proxy performance to SparrowDoor could also be a touch that the group is following the pattern of China-aligned risk actors constructing and utilizing operational relay box (ORB) networks.
Modular SparrowDoor
The modular model of SparrowDoor is considerably completely different from the earlier ones. On the community communication facet, the command header is distributed individually from the physique and that knowledge is RC4 encrypted with the hardcoded key iotrh^%4CFGTj. The customized courses used for community communication on this model nonetheless use Winsock TCP sockets and are similar to these we talked about beforehand – essentially the most notable distinction being that the kid class is deceptively named CShttps as a substitute of CTcpSocket. As seen in Desk 3, of the instructions current in earlier variations of SparrowDoor, this one solely implements the instructions that relate to managing the C&C configuration and uninstalling the backdoor. Details about the host machine is distributed robotically after the preliminary connection message and features a listing of put in safety merchandise along with what was despatched in earlier variations.
The entire different instructions are associated to the dealing with of plugins. We imagine that the eliminated performance has merely been moved to a number of modules. Whereas now we have but to watch any such plugin, we will share insights primarily based on our evaluation of the code that implements this performance.
Desk 3. Instructions carried out within the modular model of SparrowDoor
| Command ID | Response ID | Description |
| N/A | 0x136433 | Preliminary connection. |
| N/A | 0x0A4211 | Ship host info. |
| 0x3A72 | 0x0A4214 | Get present community configuration. |
| 0x3A73 | No response | Set community configuration. |
| 0x3A75 | 0x136434 | Provoke plugin command loop. See the Plugins subsection. |
| 0x3A76 | 0x136435 / 0x0A4217 | |
| 0x3A77 | 0x136435 / 0x0A421F | |
| 0x3A78 | 0x136435 / 0x0A4221 | |
| 0x3A7B | 0x136435 / 0x0A4228 | |
| 0x3A7A | No response | Uninstall backdoor and clear up. |
Plugins
Put in plugins are referenced through a typical C++ listing; every entry consists of a bitmask and a handler operate handle. The bitmask is used to find out which command IDs are dealt with by the plugin and corresponds to the low nibble of the third byte of the command ID (i.e., CommandID & 0xF0000).
This model of SparrowDoor can use 5 completely different command IDs to invoke plugin instructions. Of these, three (0x3A76, 0x3A77, and 0x3A7B) observe virtually precisely the identical path within the code – the one distinction being the response ID of the acknowledgment message. There are some very minor variations within the handshake course of between this set of instructions and the opposite two. Nonetheless, in all instances, the command is parallelized utilizing the identical methodology we described within the Commands part. On the brand new socket, the backdoor sends the corresponding response ID, the distinctive host ID, and the info it initially acquired from the C&C server. This knowledge seems to operate just like the operation ID talked about within the File operations part. After this handshake is accomplished, all 5 instructions name the identical operate to really deal with the plugin command. This operate receives the command ID and knowledge from the C&C server, then iterates by way of put in plugins to dispatch the command to the proper handler. The method is repeated till the backdoor receives an incorrectly formatted command message.
By default, just one plugin, with a bitmask of 0x10000, is put in. This plugin handles the set up of latest plugins despatched by the C&C server. Plugins are despatched by the server as PE recordsdata and are by no means saved on disk. Coupled with the diminished operate set current within the base backdoor, that is most likely meant to evade detection. After such a plugin is acquired, it’s manually mapped in reminiscence and its fmain export is known as. This operate returns a pointer to a construction containing the handle of a operate that returns the bitmask for the plugin and the handle of the handler operate. If no put in plugin has the identical bitmask, the newly acquired plugin is added to the listing.
Hyperlinks to earlier variations
We’ve got additionally recognized older samples that current important code overlaps with this modular model, together with comparable code to deal with plugins. These samples correspond to the backdoor that Pattern Micro named HemiGate in an August 2023 article. Among the samples even use the identical RC4 key talked about in that article. Moderately than being despatched by the C&C, plugins are carried out as C++ courses inheriting from an summary class named PluginInterface. These plugins observe the identical sample described within the earlier paragraph: they’ve a technique that returns a bitmask, used to dispatch instructions, and a second methodology to deal with instructions. We imagine that HemiGate represents an earlier step within the evolution of the modular backdoor. Thus, it’s probably that the plugins contained therein are consultant of these used within the newer modular model. Desk 4 presents an outline of the plugins and their performance.
Desk 4. Abstract of plugins contained in HemiGate
| Bitmask | Class title | Description |
| 0x20000 | Cmd | Run a single command. |
| 0x30000 | CFile | File system operations. |
| 0x40000 | CKeylogPlug | Keylogger performance. |
| 0x50000 | CSocket5 | TCP proxy. That is similar to the performance described earlier within the Proxy part. |
| 0x60000 | CShell | Interactive shell. |
| 0x70000 | CTransf | File switch between the shopper and C&C server. |
| 0x80000 | CRdp | Take screenshots. |
| 0xA0000 | CPro | · Record operating processes. · Kill a course of. |
| 0xC0000 | CFileMoniter | Monitor file system modifications for specified directories. |
These similarities are proof that the cluster we observe as FamousSparrow at the least partially overlaps with Earth Estries. Since HemiGate pre-dates each variations of SparrowDoor detailed earlier on this report, it might even be a sign that the modular and the parallelized variations of SparrowDoor are being developed in parallel.
ShadowPad
After SparrowDoor was detected within the US sufferer’s community, it was used to execute an MFC-based loader bearing similarities to the ShadowPad loaders previously documented by Cisco Talos.
This ShadowPad loader is a DLL named imjpp14.dll, meant to be loaded through DLL side-loading by the more-than-14-year-old, official, outdated model of the Microsoft Office IME executable, imecmnt.exe, renamed to imjp14k.exe. The loader first checks whether or not its present course of is the anticipated side-loading host by performing sample matching at offset 0xE367 in-memory. As soon as this validation succeeds, the malicious DLL decrypts the file named imjp14k.dll.dat that’s positioned in the identical listing because the DLL and its side-loading host. Lastly, the decrypted payload is injected right into a wmplayer.exe course of (Home windows Media Participant).
Despite the fact that we didn’t retrieve the encrypted payload, an in-memory ShadowPad detection occurred in a wmplayer.exe course of, with impjp14k.exe as its dad or mum course of. Moreover, it related to a ShadowPad C&C server (IP: 216.238.106[.]150). Whereas we didn’t observe any ShadowPad pattern utilizing it, one of many SparrowDoor C&C servers had a TLS certificates matching a identified ShadowPad fingerprint.
Moreover, we detected ShadowPad loaders and the ShadowPad backdoor in reminiscence on a number of machines within the sufferer’s community.
Word that that is the primary time now we have noticed FamousSparrow making use of the ShadowPad backdoor.
Different instruments
In the course of the compromise, along with the varied malware talked about above, we additionally noticed the next being utilized by the risk actor:
- A fundamental batch script that dumps the registry with the next instructions:
- reg save HKLMSYSTEM C:userspublicsys.hiv,
- reg save HKLMSAM C:userspublicsam.hiv, and
- reg save hklmsecurity C:userspublicsecurity.hiv.
- Impacket or NetExec, detected by our firewall, however now we have not collected any of the instructions.
- A loader for a model of the open-source Spark RAT that was modified to incorporate code from an open-source Go shellcode loader.
We additionally seen the usage of a instrument to dump LSASS reminiscence with the undocumented MiniDumpW API operate. This instrument is break up into two DLLs saved on disk as %HOMEpercentdph.dll and %WINDIRpercentSysWOW64msvc.dll. The latter might be meant to mix in with the official libraries for Microsoft Visible C++ (MSVC) which can be saved in the identical listing. The previous is loaded through a official model of VLC’s Cache Generator (vlc-gen-cache.exe), renamed to dph.exe, and imports capabilities from the latter. Since VLC plugins might be native DLLs, its cache generator naturally incorporates code to load and execute such libraries.
Community infrastructure
The ShadowPad C&C server makes use of a self-signed TLS certificates, with a SHA-1 fingerprint of BAED2895C80EB6E827A6D47C3DD7B8EFB61ED70B, that makes an attempt to spoof these utilized by Dell. This follows the format that was described by Hunt Intelligence in an article from February 2024. Whereas this sample can be utilized to trace ShadowPad servers, it’s not linked to any particular risk actor. One of many C&C servers utilized by SparrowDoor (45.131.179[.]24:80) had a TLS certificates, on port 443, with the identical Widespread Title (CN) because the certificates utilized by the aforementioned ShadowPad C&C server. This server can be the one one which was current in each variations of SparrowDoor.
We noticed three distinctive SparrowDoor C&C servers on this marketing campaign, all of which used port 80. The modular pattern was configured with amelicen[.]com as its third C&C server. When the pattern was first detected, this area pointed to the IP handle talked about within the earlier paragraph. One of many C&C servers configured within the modular pattern (43.254.216[.]195:80) was additionally utilized by the SparrowDoor loader. That is unusual, since SparrowDoor makes use of plain TCP and the recordsdata had been downloaded over HTTP. Nonetheless, there’s a hole of virtually two weeks between the downloads, on June 30, 2024, and the compilation of the modular SparrowDoor, on July 12, 2024. We have no idea whether or not the service listening on that port was modified between these two occurrences or whether or not the SparrowDoor C&C server contains performance to serve recordsdata over HTTP.
Conclusion
Because of the lack of exercise and public reporting between 2022 and 2024, FamousSparrow was presumed to be inactive. Nonetheless, our evaluation of the US community compromised in July 2024 revealed two new variations of SparrowDoor, displaying that FamousSparrow continues to be growing its flagship backdoor. One among these new variations was additionally discovered on a machine in Mexico. As we had been organising monitoring primarily based on what is roofed on this blogpost, we uncovered further exercise by the group throughout this era, together with the concentrating on of a governmental establishment in Honduras. This newly discovered exercise signifies that not solely is the group nonetheless working, nevertheless it was additionally actively growing new variations of SparrowDoor throughout this time.
We are going to proceed to watch and report on exercise by FamousSparrow, and also will proceed to observe the dialogue surrounding potential hyperlinks between FamousSparrow and Salt Storm.
For any inquiries about our analysis revealed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.ESET Analysis presents non-public APT intelligence reviews and knowledge feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Threat Intelligence web page.
IoCs
Recordsdata
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| C26F04790C6FB7950D89 |
DotNetNuke.ashx | ASP/Webshell.SE | ASHX webshell. |
| F35CE62ABEEDFB8C6A38 |
DrmUpdate.exe | N/A | Reputable Microsoft Workplace IME 2010 used for DLL side-loading. |
| 5265E8EDC9B5F7DD00FC |
imjp14k.dll | Win32/Agent.AGOZ | ShadowPad loader. |
| A91B42E5062FEF608F28 |
dph.exe | N/A | Reputable VLC cache generator. |
| 0DC20B2F11118D5C0CC4 |
vlc.exe | N/A | Reputable VLC media participant used for DLL side-loading. |
| EF189737FB7D61B110B9 |
libvlc.dll | Win64/Agent.FAY | SparrowDoor loader. |
| D03FD329627A58B40E80 |
notify.exe | N/A | Reputable Yandex software used for DLL side-loading. |
| 3A395DAAF518BE113FCF |
WINMM.dll | Win32/Shellcode |
Loader for modular SparrowDoor. |
| 0925F24082971F50EDD9 |
WindowsUpdate.exe | N/A | Reputable Fortemedia Audio Processing used for DLL side-loading. |
| 5F1553F3AF9425EF5D68 |
FmApp.dll | Win64/Agent.EEA | ShadowPad loader. |
| CC350BA25947B7F9EC5D |
FmApp.dll | Win64/Agent.EDQ | ShadowPad loader. |
| DB1591C6E23160A94F63 |
K7AVWScn.exe | N/A | Reputable K7AntiVirus Messenger Scanner Stub used for DLL side-loading. |
| 1B06E877C2C12D74336E |
K7AVWScn.dll | Win32/Agent.AGOJ | SparrowDoor loader. |
| EBC93A546BCDF6CC1EB6 |
begin.bat | BAT/Agent.DP | Batch script to deploy the ASHX webshell. |
| D6D32A1F17D48FE695C0 |
dph.dll | Win64/Riskware. |
Program to dump LSASS reminiscence. |
| 7D66B550EA68A86FCC09 |
Ntmssvc.dll | WinGo/Shellcode |
Modified Spark RAT. |
| D78F353A70ADF68371BC |
N/A (in-memory) | Win32/Agent.VQI | Decrypted SparrowDoor payload. |
| 99BED842B5E222411D19 |
N/A (in-memory) | Win32/Agent.VQI | Decrypted modular SparrowDoor payload. |
| 5DF3C882DB6BE1488718 |
taskhosk.exe | Win32/Agent.AHCV | SparrowDoor/HemiGate with built-in plugins. |
| AA823148EEA6F43D8EB9 |
taskhosk.exe | Win32/Agent.AHCV | SparrowDoor/HemiGate with built-in plugins. |
Community
| IP | Area | Internet hosting supplier | First seen | Particulars |
| 43.254.216[.]195 |
N/A | Hongkong Wen Jing Community Restricted | 2024‑06‑27 | FamousSparrow C&C and obtain server. |
| 45.131.179[.]24 |
amelicen |
XNNET LLC | 2024‑07‑05 | SparrowDoor C&C server. |
| 103.85.25[.]166 |
N/A | Starry Community Restricted | 2024‑06‑06 | SparrowDoor C&C server. |
| 216.238.106[.]150 |
N/A | Vultr Holdings, LLC | 2024‑03‑11 | ShadowPad C&C server. |
MITRE ATT&CK strategies
This desk was constructed utilizing version 16 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
| Tactic | ID | Title | Description |
| Useful resource Improvement | T1588.001 | Get hold of Capabilities: Malware | FamousSparrow acquired and used ShadowPad. |
| T1588.002 | Get hold of Capabilities: Software | FamousSparrow acquired the open-source PowerHub post-exploitation framework. | |
| T1588.005 | Get hold of Capabilities: Exploits | FamousSparrow added the BadPotato exploit to its deployment of PowerHub. | |
| T1583.004 | Purchase Infrastructure: Server | FamousSparrow acquired a server to host malware and instruments. | |
| T1584 | Compromise Infrastructure | Servers compromised with SparrowDoor might be compelled to operate as proxies. | |
| T1608.001 | Stage Capabilities: Add Malware | FamousSparrow hosted SparrowDoor by itself server. | |
| T1608.002 | Stage Capabilities: Add Software | FamousSparrow uploaded PowerHub to a server it controls. | |
| T1587.001 | Develop Capabilities: Malware | FamousSparrow developed new variations of SparrowDoor. | |
| Preliminary Entry | T1190 | Exploit Public-Going through Utility | FamousSparrow probably exploited a vulnerability in an outdated Trade server to achieve preliminary entry. |
| T1078.002 | Legitimate Accounts: Area Accounts | FamousSparrow used legitimate credentials for a website account to pivot to different machines in compromised networks. | |
| Execution | T1059.001 | Command-Line Interface: PowerShell | FamousSparrow used an interactive PowerShell session to carry out reconnaissance and deploy SparrowDoor. |
| T1059.003 | Command-Line Interface: Home windows Command Shell | SparrowDoor can launch cmd.exe to create a distant shell session. | |
| T1106 | Native API | SparrowDoor makes use of the CreateProcess API to launch an interactive shell. | |
| T1047 | Home windows Administration Instrumentation | FamousSparrow used wmic.exe to run reconnaissance instructions. | |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | SparrowDoor can create a Run key to persist on a compromised system. |
| T1543.003 | Create or Modify System Course of: Home windows Service | SparrowDoor can create a service to persist on a compromised system. | |
| T1505.003 | Server Software program Element: Net Shell | FamousSparrow deployed webshells to compromised servers. | |
| Privilege Escalation | T1068 | Exploitation for Privilege Escalation | FamousSparrow used the BadPotato exploit to achieve SYSTEM privileges. |
| Protection Evasion | T1055 | Course of Injection | SparrowDoor injects its loader right into a Home windows coloration administration course of. |
| T1055.001 | Course of Injection: Dynamic-link Library Injection | The ShadowPad loader injects its payload right into a newly created Home windows Media Participant course of. | |
| T1574.002 | Hijack Execution Circulate: DLL Aspect-Loading | The SparrowDoor loader is executed by side-loading from a official K7 Antivirus executable. | |
| T1140 | Deobfuscate/Decode Recordsdata or Info | SparrowDoor’s encrypted C&C server configuration is decrypted at runtime. | |
| T1564.001 | Conceal Artifacts: Hidden Recordsdata and Directories | FamousSparrow has used attrib.exe to set the hidden and system file attributes on the SparrowDoor loader. | |
| T1564.003 | Conceal Artifacts: Hidden Window | SparrowDoor launches the method into which it injects the loader, with its window hidden. | |
| T1070.004 | Indicator Elimination: File Deletion | SparrowDoor can uninstall itself, which incorporates deleting the related recordsdata. | |
| T1070.009 | Indicator Elimination: Clear Persistence | SparrowDoor can uninstall itself, which removes any persistence. | |
| T1027.009 | Obfuscated Recordsdata or Info: Embedded Payloads | FamousSparrow used a batch script that deploys an embedded ASPX webshell. | |
| T1027.010 | Obfuscated Recordsdata or Info: Command Obfuscation | PowerHub obfuscates components of its instructions by encrypting them with RC4. | |
| T1027.013 | Obfuscated Recordsdata or Info: Encrypted/Encoded File | The file containing the SparrowDoor payload is RC4 encrypted. | |
| T1036.004 | Masquerading: Masquerade Job or Service | The outline and title of the service utilized by SparrowDoor to persist match these of the official K7 program it’s impersonating. | |
| T1036.005 | Masquerading: Match Reputable Title or Location | The SparrowDoor loader masquerades as a DLL loaded by the official K7AVWScn.exe. | |
| T1036.008 | Masquerading: Masquerade File Kind | The encrypted payload file containing SparrowDoor has a .doc extension. | |
| T1620 | Reflective Code Loading | The modular model of SparrowDoor can load further PE recordsdata into its personal reminiscence area. | |
| Credential Entry | T1003.001 | OS Credential Dumping: LSASS Reminiscence | FamousSparrow used a utility to dump LSASS reminiscence. |
| Discovery | T1482 | Area Belief Discovery | FamousSparrow used nltest.exe to listing area controllers and trusted domains. |
| T1087.001 | Account Discovery: Native Account | FamousSparrow used web.exe to acquire info on native accounts. | |
| T1087.002 | Account Discovery: Area Account | FamousSparrow used web.exe to acquire info on area accounts. | |
| T1049 | System Community Connections Discovery | FamousSparrow used netstat.exe to listing lively TCP connections. | |
| T1083 | File and Listing Discovery | SparrowDoor can listing directories. | |
| T1057 | Course of Discovery | FamousSparrow used tasklist.exe to listing operating processes and providers, and to search out the LSASS course of. | |
| T1012 | Question Registry | FamousSparrow used a script to dump the SAM, SYSTEM, and SECURITY registry hives. | |
| T1082 | System Info Discovery | FamousSparrow used wmic.exe to acquire details about mapped drives. It additionally used ipconfig.exe to listing community adapters. | |
| T1033 | System Proprietor/Person Discovery | FamousSparrow used whoami.exe to acquire details about the lively consumer and their privileges. | |
| T1518.001 | Software program Discovery: Safety Software program Discovery | The modular model of SparrowDoor lists put in safety software program. | |
| Lateral Motion | T1570 | Lateral Software Switch | FamousSparrow transferred SparrowDoor to different machines on the community. |
| T1021 | Distant Providers | FamousSparrow has used distant PowerShell classes to pivot onto different machines within the compromised community. | |
| Assortment | T1005 | Knowledge from Native System | SparrowDoor can learn recordsdata from any native system drive. |
| T1025 | Knowledge from Detachable Media | SparrowDoor can learn recordsdata from any mapped detachable drive. | |
| T1039 | Knowledge from Community Shared Drive | SparrowDoor can learn recordsdata from any mapped community shared drive. | |
| Command and Management | T1095 | Non-Utility Layer Protocol | SparrowDoor makes use of uncooked TCP sockets to speak with its C&C server. |
| T1071.001 | Utility Layer Protocol: Net Protocols | FamousSparrow downloaded further recordsdata from its C&C server over HTTP. | |
| T1573.001 | Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography | Within the modular model of SparrowDoor, knowledge despatched over the community is RC4 encrypted. | |
| T1008 | Fallback Channels | SparrowDoor can have as much as three C&C servers in its community configuration. | |
| T1105 | Ingress Software Switch | FamousSparrow downloaded PowerHub from a server it controls. | |
| T1571 | Non-Customary Port | FamousSparrow downloaded PowerHub over HTTP on port 8080 and over HTTPs on port 8443. | |
| Exfiltration | T1020 | Automated Exfiltration | SparrowDoor can exfiltrate the content material of any file requested by the C&C server. |
| T1030 | Knowledge Switch Measurement Limits | SparrowDoor splits file content material into chunks of 4 kB. | |
| T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | SparrowDoor exfiltrates knowledge utilizing the identical uncooked TCP socket it makes use of to speak with its C&C server. |




